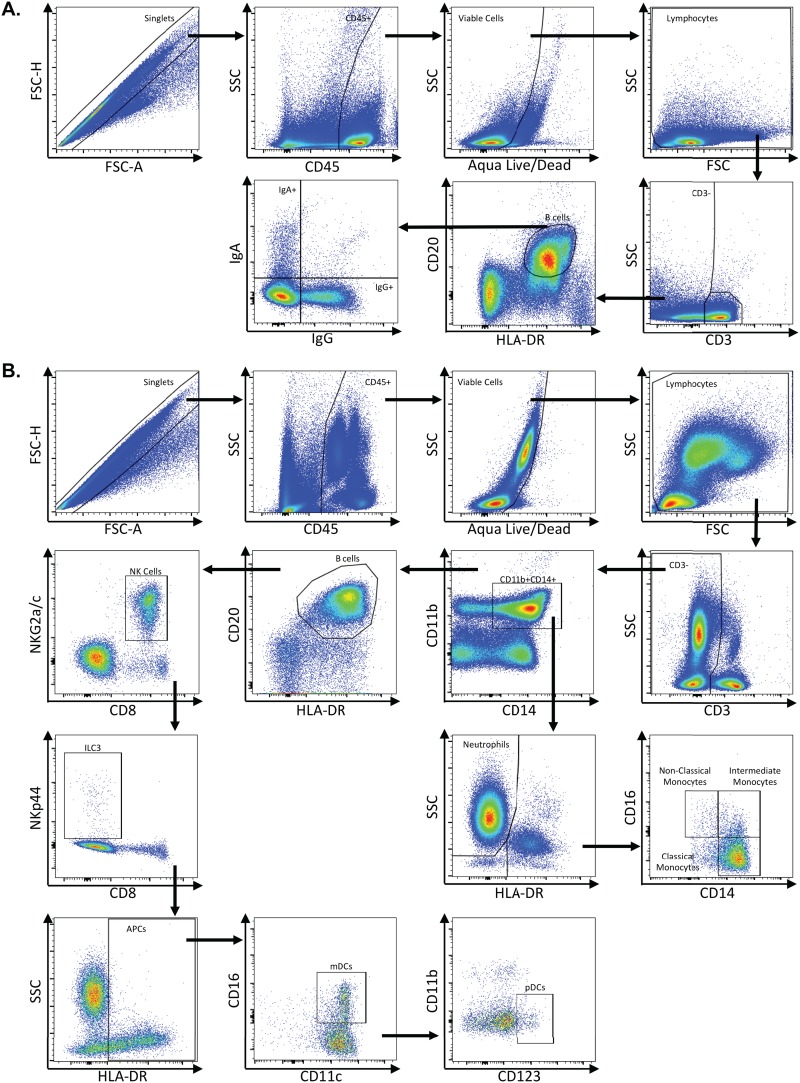
FIG 11.
Representative flow plots demonstrating gating strategy used to identify B cells and innate immune subsets. Multicolor flow cytometry was used to identify B cells and innate immune subsets in whole blood, lymph node, rectum, and colon cells. (A) Depicted here are representative plots of stained lymph node cells from an uninfected rhesus macaque. Cells were identified by first excluding doublets using forward scatter (FSC) area and height properties, gating on CD45+ cells, excluding dead cells using an Aqua Live/Dead viability dye, and removing any remaining debris using FSC and side scatter (SSC) properties. Next, CD3− cells were identified, and B cells were gated as CD20+ HLA-DR+ cells. IgA- and IgG-expressing B cells were identified within CD20+ HLA-DR+ B cells. (B) Innate immune subsets, including neutrophils, monocytes, NK cells, ILC3s, mDCs, and pDCs, were identified in colon or whole blood. Depicted here are representative plots of stained whole blood cells from an uninfected rhesus macaque. As with B cells, cells were identified by excluding doublets using FSC area and height, gating on CD45+ cells, excluding dead cells, and removing debris with FSC/SSC properties. Next, CD3− cells were identified, and neutrophils were gated as CD11b+ CD14+ HLA-DR− SSChi cells. Monocytes were identified as CD11b+ CD14+ HLA-DR+ cells and then further classified as classical monocytes (CD14+ CD16−), intermediate monocytes (CD14+ CD16+), and nonclassical monocytes (CD14+ CD16+). After excluding CD11b+ CD14+ cells, B cells were excluded by gating out HLA-DR+ CD20+ cells, and then NK cells were identified as NKG2a/c+ CD8+. After excluding NK cells, ILC3s were identified as NKp44+ CD8−. After excluding ILC3s, antigen-presenting cells were identified as HLA-DR+ and further classified as mDCs (CD11c+) and pDCs (CD123+).