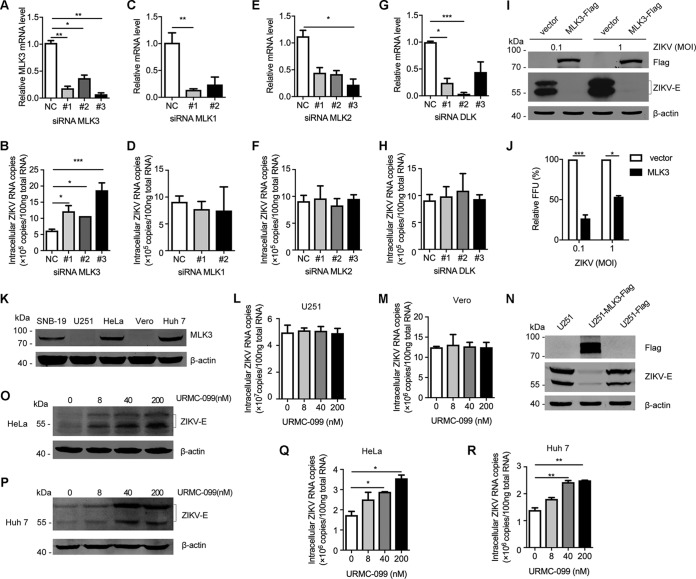
FIG 4.
Confirmation of MLK3 as a key regulator of ZIKV infection. (A) MLK3-specific siRNAs (50 nM) were transiently transfected into SNB-19 cells. MLK3 mRNA levels were determined by qRT-PCR. (B) Viral RNA was quantified by qRT-PCR after 72 h of infection in SNB-19 cells that were transfected with MLK3 siRNAs 36 h before ZIKV (MOI = 0.1) infection. A scrambled siRNA was used as a negative control. (C to H) Knockdown of MLK1, MLK2, and DLK and its effects on ZIKV infection. (I and J) SNB-19 cells stably transfected with a plasmid overexpressing MLK3 or vector control cells were infected with ZIKV (MOI = 0.1 or 1) for 48 h, and virus propagation was analyzed by Western blotting (I) or FFU assay (J). (K) Endogenous MLK3 expression profiles were analyzed by Western blotting in SNB-19, U251, HeLa, Vero, and Huh7 cells. (L and M) The effects of URMC-099 on MLK3-defecient U251 and Vero cells. (N) ZIKV infection was inhibited in U251 cells stably expressing MLK3. (O to R) Characterization of the effects of URMC-099 on ZIKV infection (MOI = 0.1) in HeLa and Huh7 cells with endogenous MLK3 by Western blotting (O and P) and qRT-PCR (Q and R).