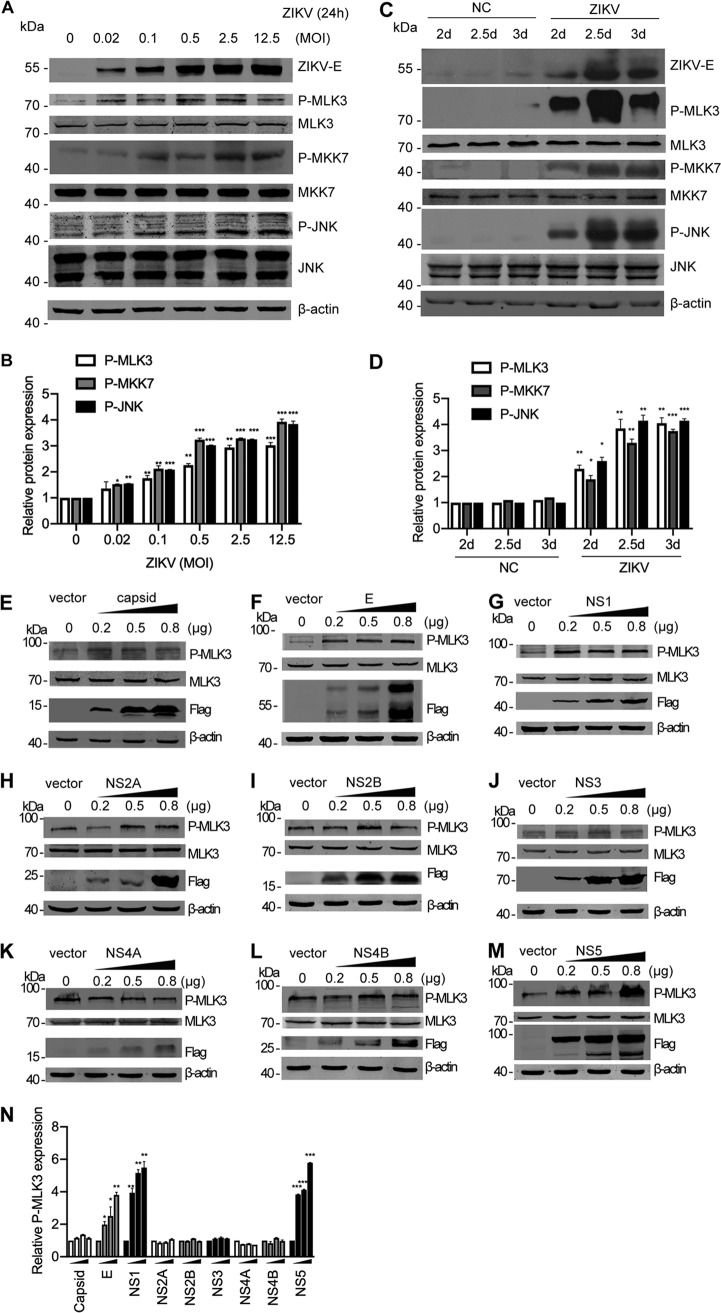
FIG 8.
ZIKV infection activates the MLK3/MKK7/JNK pathway. (A) SNB-19 cells were infected with ZIKV (MOI = 0.02, 0.1, 0.5, 2.5, and 12.5) for 24 h. Cell lysates were subjected to Western blotting with the indicated antibodies. The same blots were reprobed with an anti-β-actin antibody to ensure equal loading. (B) Bands of the phosphorylated MLK3, MKK7, and JNK in panel A were quantified with ImageJ software; fold change is shown. The phosphorylated proteins were normalized to corresponding nonphosphorylated proteins to indicate their phosphorylation levels. (C) The ZIKV SZ01 strain was intracerebrally injected into neonatal BALB/c mice on day 0 after birth. “NC” represents PBS injection as a negative control. Brain tissues were collected at 2, 2.5, or 3 days postinfection (dpi), and Western blotting was performed with the indicated antibodies. (D) Bands of the phosphorylated MLK3, MKK7, and JNK in panel C were quantified. (E to M) SNB-19 cells in 24-well plates were transfected with individual Flag-tagged ZIKV protein constructs (0.2, 0.5, or 0.8 μg each well). Western blotting was performed to measure phosphorylated MLK3, MLK3 total protein, and Flag-tagged viral proteins. β-Actin was used as an equal loading control. (N) Western blotting bands in Fig. 8E to M were quantified as fold change.