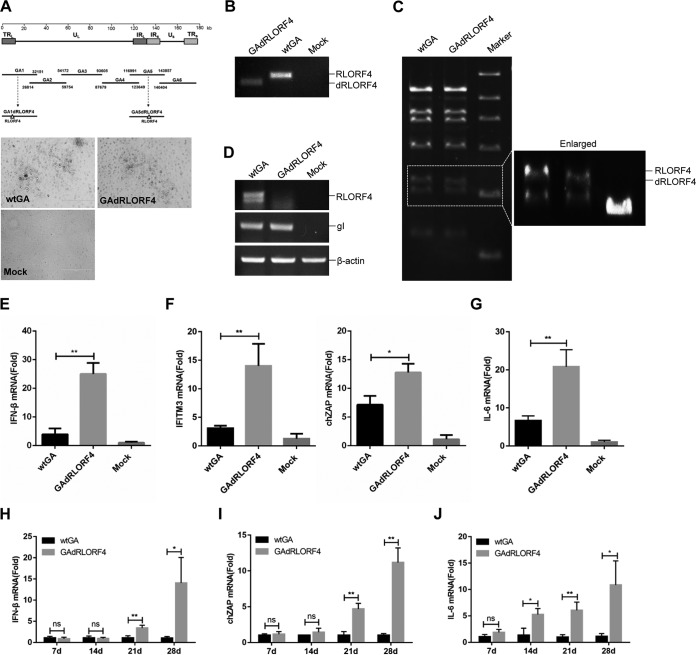
FIG 5.
RLORF4 deficiency enhances MDV-triggered IFN-β production in vitro and in vivo. (A) Schematic diagram of the recombinant fosmids for constructing recombinant MDVs (top) and the cytopathic effects induced by wtGA and GAdRLORF4 in DEFs (bottom). Bar length, 400 μm. (B) PCR analyses of the RLORF4-deficient MDV. (C) Pulsed-field gel electrophoresis analysis of the wtGA and GAdRLORF4 virus DNAs digested with BamHI. (D) Reverse transcription-PCR (RT-PCR) for RLORF4, gI, and β-actin mRNA expression was performed using total RNA collected from wtGA- or GAdRLORF4-infected cells. (E to G) CEFs were infected with wtGA or GAdRLORF4 (MOI = 0.1) for 12 h before the analysis of IFN-β (E), ZAP and IFITM3 (F), and IL-6 (G) mRNA levels. (H to J) Chickens were infected with 2,000 PFU of wtGA or GAdRLORF4. IFN-β (H), ZAP (I), and IL-6 (J) production in chickens was measured by qPCR at the indicated time points after MDV infection. Statistical analysis was performed with Student’s t test (*, P < 0.05, **, P < 0.01; ns, no significant difference).