FIG 2.
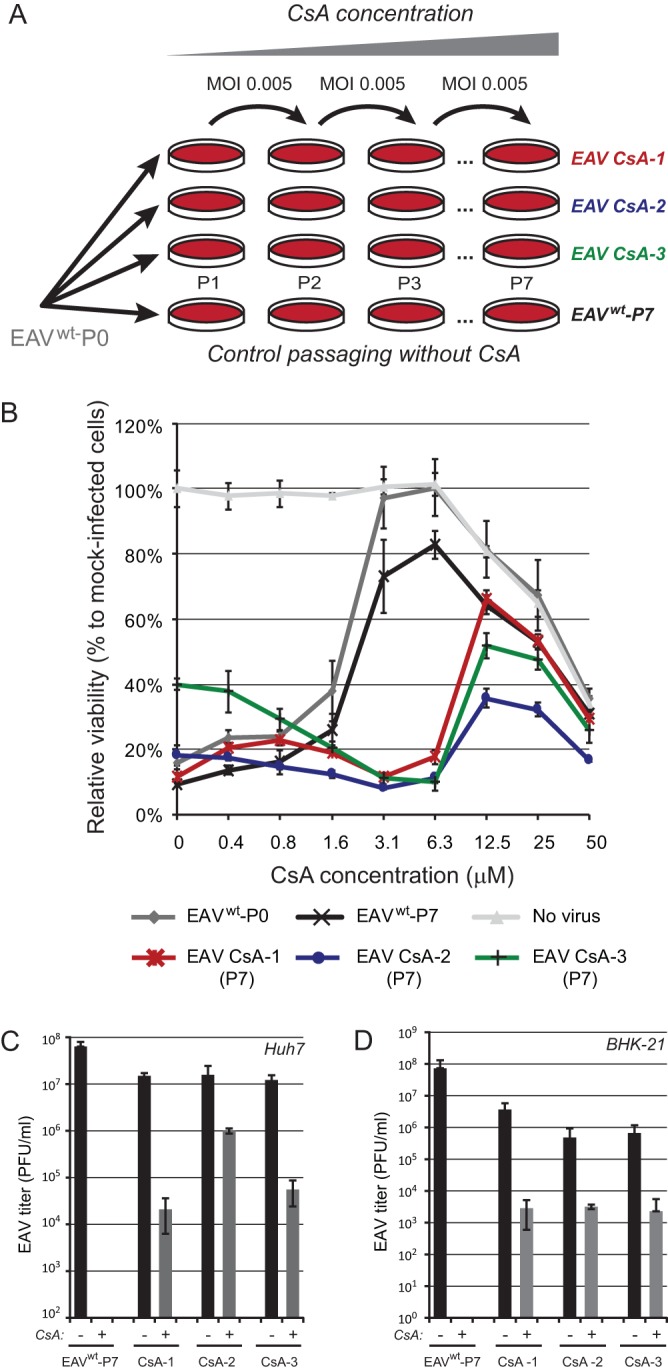
Selection of CsA-resistant EAV mutants. (A) Passaging scheme for wild-type (wt) EAV (strain Bucyrus) in Huh7 cells (MOI, 0.005) to generate three independent CsA-resistant replicates (EAV CsA-1, CsA-2, and CsA-3). Passaging was performed in the presence of increasing CsA concentrations, ranging from 4 μM during passage 1 (P1) to 20 μM during P7. As a control, EAVwt was passaged in the absence of CsA to assess the acquisition of mutations unrelated to CsA resistance. (B) After P7, EAV CsA-1 (red), CsA-2 (blue), and CsA-3 (green) were tested for CsA resistance, while including the original (P0, gray) and passaged (P7, black) EAVwt as controls. Huh7 cells in 96-well plates were infected at an MOI of 0.05 in the presence of 0 to 50 μM CsA. Cells were incubated for 3 days and cell viability was monitored using a commercial assay. Furthermore, the cytotoxicity of CsA treatment only was monitored in parallel in mock-infected Huh7 cells (light gray). Graphs show the results (averages and SD) of a representative experiment performed in quadruplicate. All experiments were repeated at least twice. Huh7 cells (C) or BHK-21 cells (D) were infected with EAV CsA-1, -2, or -3 or with lineage EAVwt P7 (MOI, 0.01). At 1 h p.i., the inoculum was replaced by medium containing either 0.02% DMSO (bars labeled “−”; solvent control) or 4 μM CsA (bars labeled “+”). Medium was collected at 32 h p.i., and EAV progeny titers were determined by plaque assay.
