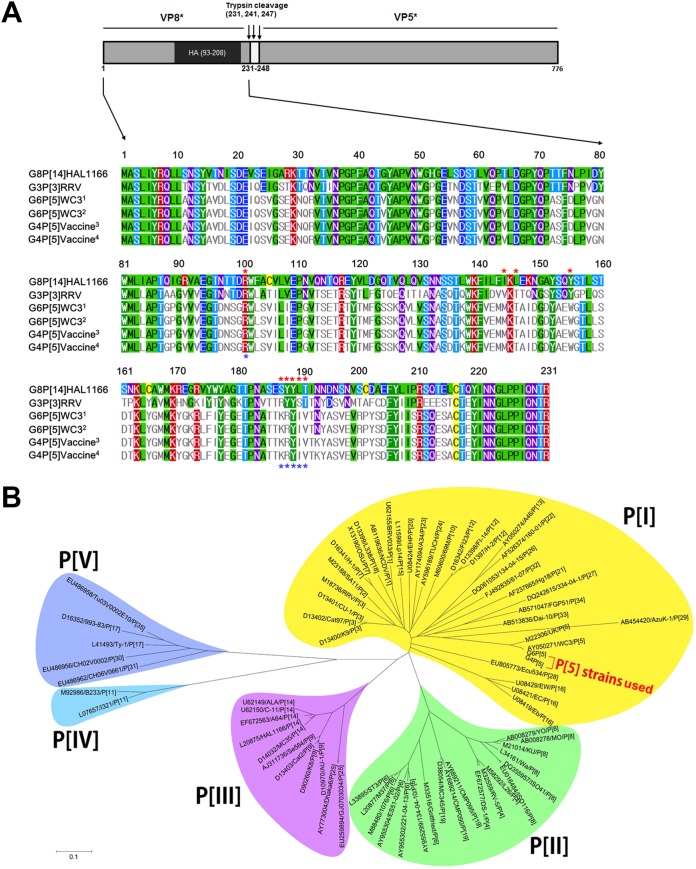
FIG 1.
Full-length VP8* amino acid sequence and phylogenetic analyses. (A) Structural features of the VP8* domain of the spike protein VP4 shows the VP8* (left) and VP5* (right) domains with trypsin cleavage sites. The VP8* domains of the original GenBank-deposited WC3 (G6P[5] WC3 marked by a superscript 1) and RotaTeq (G4P[5] RotaTeq marked by a superscript 3) strains, and G6P[5] (marked by a superscript 2) and G4P[5] RotaTeq (marked by a superscript 4) strains used in this study, and control G3P[3] RRV and G8P[14] HAL1166 strains were 231 amino acids in length. The VP8* hemagglutination (HA) domain (amino acids 93 to 208) is shown in the schematic diagram. In the multiple sequence alignment, the amino acids at the sialic acid (SA) binding site of P[I] strains (see panel B) are marked with red asterisks (amino acids 101, 144, 146, 155, and 187 to 190). Amino acids at the blood group A binding site of P[III] strains are marked with blue asterisks (amino acids 101 and 187 to 190). The information regarding the SA and HBGA binding sites is from Isa et al. (26) and Hu et al. (27). The full-length VP8* amino acid sequences of the bovine G6P[5] WC3 strain and bovine-human mono-reassortant G4P[5] strain used in this study show only one amino acid substitution at residue 193 (N193K). (B) Phylogenetic analysis of the full-length VP8* amino acid sequence was performed using the neighbor-joining method. Note that the VP8* domain of both strains used in this study belongs to the P[I] genogroup, which is closely related to the GenBank-registered WC3 strain. Sequence information for the 71 selected strains is shown in the order of GenBank accession number, strain name, and P genotype. Calibration bar indicates the nucleotide substitutions per site.