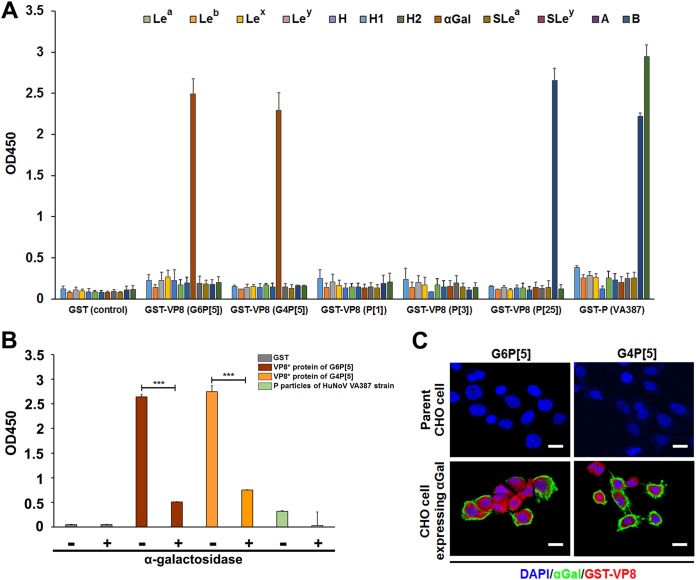
FIG 3.
Binding of the recombinant VP8* domain of bovine G6P[5] WC3 and bovine-human mono-reassortant G4P[5] strains to synthetic histo-blood group antigens (HBGAs) and CHO cells after GGTA1 transfection. (A) The binding abilities of the recombinant GST- VP8* domains corresponding to P[5], P[1], P[3], and P[25] RVA strains and the GST-P domain of human norovirus strain VA387 (GII.4) were determined using horseradish peroxidase (HRP)-conjugated streptavidin. HBGA binding was visualized using TMB, which was measured at 450 nm in three independent experiments. Error bars represent means ± the standard deviations (SD). (B) The αGal epitope was removed from the synthetic Galα3Galβ4GlcNAcβ HBGA using α-galactosidase. The binding specificity to the VP8* domain of the bovine G6P[5] WC3 and bovine-human mono-reassortant G4P[5] strains and to P particles of the human norovirus VA387 strain was determined using an HBGA binding assay. (C) Mock-transfected parent CHO cells or GGTA1-transfected CHO cells were coincubated with FITC-conjugated anti-αGal MAb and AF594-labeled VP8* proteins of either G6P[5] WC3 or G4P[5] RotaTeq vaccine strains. No labeling was visible on mock-transfected CHO cells that lack αGal, while both VP8* and the anti-αGal antibodies stained the GGTA1-transfected cells. The VP8* and the MAb labeling did not overlap, likely due to competition for the same ligand. Nuclei were stained with DAPI. Scale bars, 20 μm.