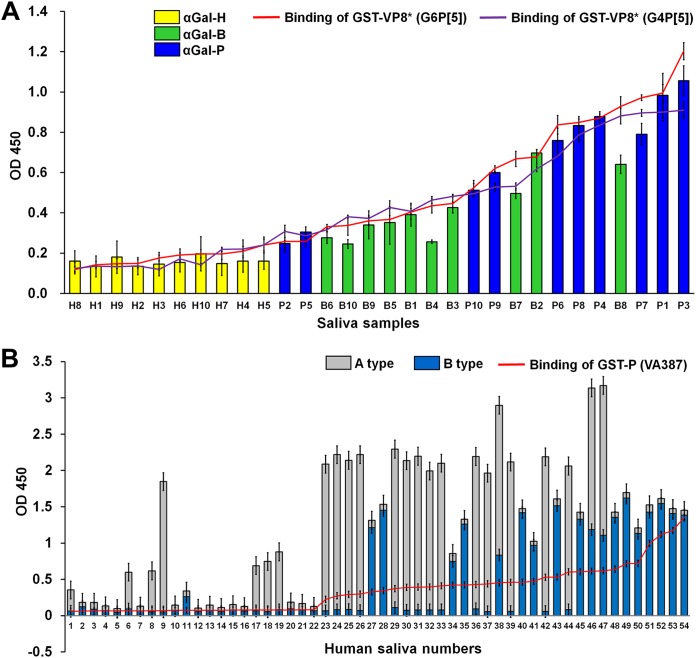
FIG 4.
Binding of recombinant VP8* domain of bovine G6P[5] WC3 and bovine-human mono-reassortant G4P[5] strains to saliva. (A) Binding of the GST-VP8* domains was tested on a panel of human, bovine, and porcine saliva samples, using an anti-GST antibody (1:1,000 dilution), followed by the addition of an HRP-conjugated goat anti-mouse IgG antibody. The binding results to individual saliva samples were sorted by the αGal signals of individual saliva samples. A trend for correlation between the salivary αGal signals and VP8* binding levels for both P[5]-bearing strains was observed. Capital letters H, P, and B on the x axis identifies human (indicated by yellow bars), pig (indicated by blue bars), and cow (indicated by green bars) samples, respectively. (B) GST-P domain of norovirus strain VP387 (GII0.4) was tested as a positive control for binding to a panel of saliva samples from 54 human individuals. The A and B type signals of each individual saliva sample were sorted particularly based on the stronger intensity of A type signal, and the binding activity of the P domain to each individual saliva sample was plotted on a graph. A trend for correlation with the salivary A and B signals with the binding levels of the P domain was observed. The binding ability of recombinant GST-VP8* domains or GST-P domain was determined by the saliva-binding assay mentioned above. The binding of the saliva samples was visualized using TMB and measured at 450 nm in three independent experiments. Error bars represent means ± the SD.