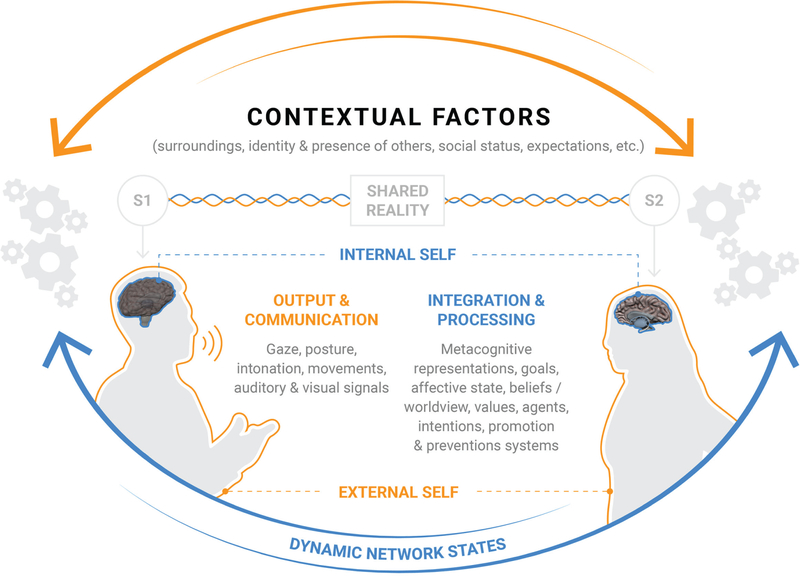
Fig. 1.
Representation of components and processes during a conventional social exchange. Speaker 1 (S1), the sender, provides multimodal information in the form of sensory cues such as intonation, language, intensity, timing of verbal exchange and movements, posture, and gaze as signals. Speaker 2 (S2), the receiver, must recruit perceptual, inferential, learning, and other domain-general systems to generate and operate on an accurate interpretation of the signals. External influences such as context and internal influences, including goals and affective and motivational states, modulate processing in domain-general and social-cognitive systems.