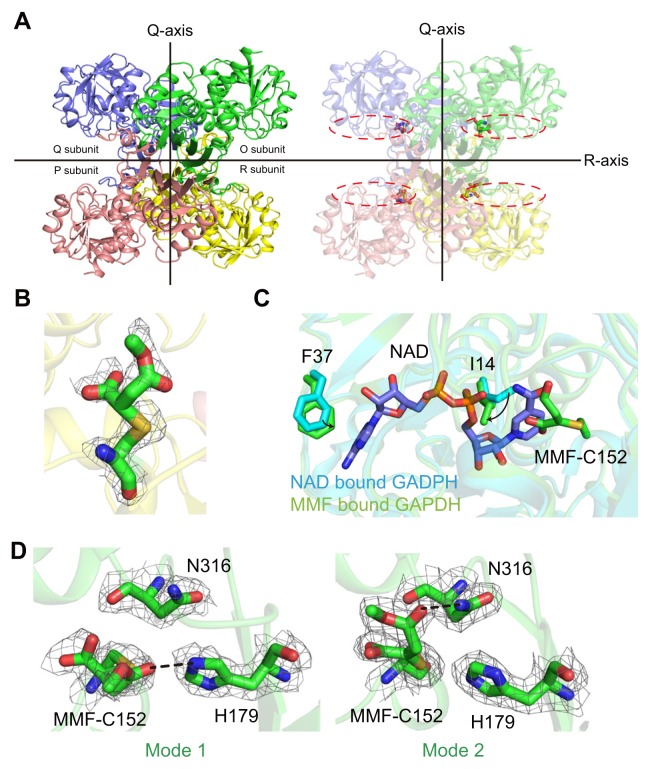
Fig. 2. Overall structure and MMF binding mode in the GAPDH active site.
(A) The crystal structure shows that MMF-bound hGAPDH has a tetrameric structure based on the Q and R axes (the P axis is not presented). The dotted line represents the NAD+ binding site of hGAPDH. (B) The Fo-Fc electron density map (contour 1.0 σ) for covalently linked MMF with Cys152 of hGAPDH. (C) Comparison of the NAD+ binding site between NAD+-bound hGAPDH and MMF-bound hGAPDH. Two molecules are superimposed based on the C-α carbon of the protein backbone. (D) Two different binding modes of MMF in each protomer of tetrameric hGAPDH. Hydrogen bonds are shown as black lines.