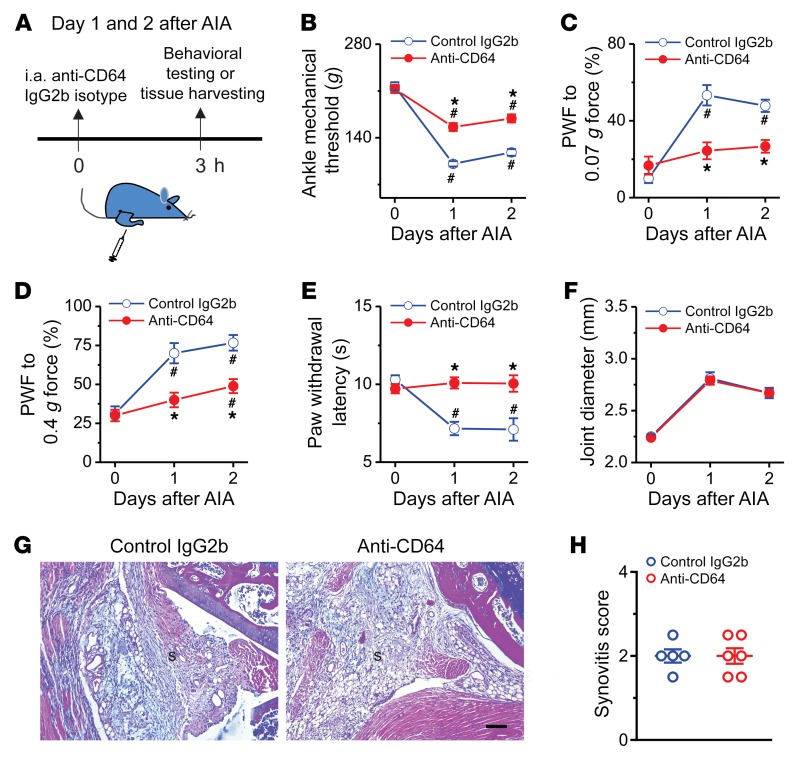
Figure 9. Acute pharmacological blockade of FcγRI attenuates AIA-associated pain in male mice.
(A) Experimental schematic indicating once-daily injection of anti-CD64 (2.25 μg; 5 μL) or IgG2b isotype control (2.25 μg; 5 μL) into knee (for histology) or ankle cavity (for behavioral testing) of mice on days 1 and 2 after AIA. Pain-related behaviors were measured within 3 hours after each injection. (B–F) Effects of repeated daily i.a. injection of anti-CD64 or IgG2b isotype control on mechanical threshold in the ankle (B), paw withdrawal frequency (PWF) in response to 0.07 g (C) and 0.4 g force (D), paw withdraw latency to radiant heat (E), and ankle joint diameter (F) in the mice with AIA. n = 9 mice per group; *P < 0.05 vs. control IgG2b isotype, #P < 0.05 vs. day 0; 2-way ANOVA for repeated measures followed by Bonferroni’s post hoc test. (G) H&E staining assessment of synovitis in the inflamed knee joint of AIA mice treated with IgG2b isotype control (n = 5 mice) or anti-CD64 (n = 6 mice). S, synovium. Scale bar: 100 μm. (H) Quantification showed no difference in synovitis score between treatment groups. P > 0.05, unpaired Student’s t test.