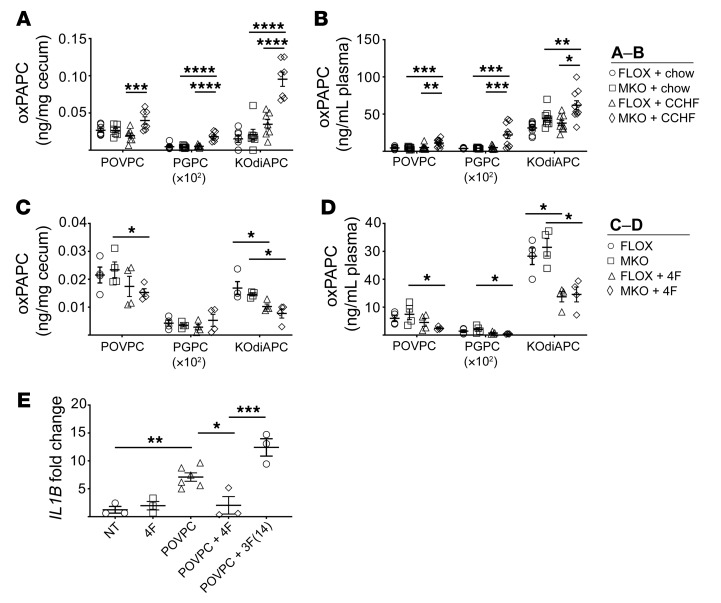
Figure 7. Oxidized PAPC is elevated in the plasma and ceca of Cox2-MKO and CCHF-fed mice, whereas 4F both reduces oxidized PAPC in vivo and inhibits oxidized PAPC-dependent proinflammatory response in human macrophages.
*P < 0.05; **P < 0.01; ***P < 0.001; ****P < 0.0001. Levels of oxPAPC products (POVPC, PGPC, and KOdiAPC) were determined in the ceca (n = 7) (A) and plasmas (n = 10) (B) of Cox2-MKO (MKO) and FLOX mice fed CCHF or chow for 8.5 weeks. Independently, the effect of 4F on oxPAPC in the ceca (C) and plasma (D) of MKO and FLOX mice fed CCHF for 3 weeks was determined. Last, human THP-1 macrophages were treated with 1 μM POVPC for 3 hours with and without the apoA-I mimetic peptides 4F and 3F(14); and expression of IL1B was determined by qPCR (n = 3–6) (fold change vs. NT) (E) After 8.5 weeks, MKO + CCHF diet significantly increased oxPAPC species in both ceca and plasma. 4F significantly lowered levels of oxPAPC in vivo, and 4F but not 3F(14) significantly inhibited the proinflammatory effect of POVPC on macrophages. For each analyte in A–D, 2-way ANOVA with Tukey’s multiple comparisons test and adjusted P values was used. A 1-way ANOVA with Tukey’s multiple comparisons test and adjusted P values was used for E.