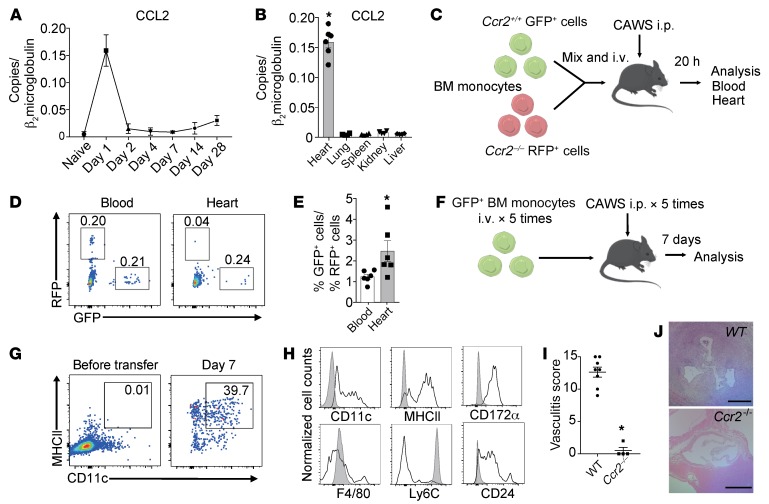
Figure 2. CCL2 is induced in the heart on day 1 and promotes CCR2+ monocyte recruitment.
(A) Kinetics of CCL2 mRNA expression in the heart following CAWS injection. (B) CCL2 expression in various organs on day 1 after CAWS injection (mean ± SEM, n = 4 mice per group, *P < 0.001 versus lung, spleen, kidney and liver). (C) Schematic of co–adoptive transfer of WT and Ccr2–/– bone marrow–derived monocytes (BMDMs) into WT mice followed by CAWS injection. Equal numbers of Ccr2+/+ GFP+ and Ccr2–/– RFP+ BMDMs were mixed and intravenously transferred into WT recipient mice along with CAWS injection daily for 5 days. Peripheral blood and heart of recipient mice were analyzed 20 hours after cell transfer. (D) Representative FACS plots of the indicated tissues 20 hours after adoptive transfer of BMDMs and CAWS injection. Ccr2+/+ GFP+ and Ccr2–/– RFP+ cells in the heart tissue are shown. Numbers indicate percentages of live CD45+ cells. (E) Ratio of Ccr2+/+ GFP+ cells/Ccr2–/– RFP+ cells in the indicated tissues (mean ± SEM, n = 6 mice, *P < 0.05 versus blood). (F) Schematic of adoptive transfer of GFP+ BMDMs into WT mice followed by CAWS injection. (G) Representative FACS plots of the CD45+GFP+ live BMDM cell population before adoptive transfer and those recovered from the heart 7 days after CAWS injection. CAWS-injected recipient mice were adoptively transferred with GFP+ BMDMs (once daily for 5 days). (H) Representative histograms of the GFP+ live cell population before adoptive transfer (filled gray) and those recovered from heart 7 days after CAWS injection (black line). (I) Histological vasculitis scores were determined in WT and Ccr2–/– mice on day 28 (mean ± SEM, *P < 0.001 versus WT). (J) H&E–stained sections of aortic root lesions from WT and Ccr2–/– mice on day 28 after CAWS injection. Scale bars: 400 μm. Data in G and H are representative of 3 independent experiments. All P values were calculated using unpaired 2-tailed Student’s t test.