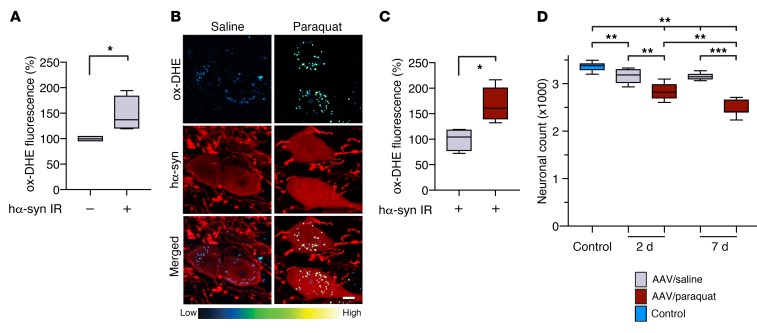
Figure 2. hα-Synuclein overexpression causes an oxidative stress that is augmented by paraquat administration.
(A) Mice (n = 4) received a unilateral (left) intravagal injection of hα-synuclein–carrying AAVs. They were then treated with 2 i.p. injections of saline and were sacrificed at 2 days after the second saline administration. They also received an injection of DHE 1 hour before the time of sacrifice. Ox-DHE fluorescent signal was compared in the left DMnX between transduced neurons immunoreactive for hα-synuclein (hα-syn IR) and neurons devoid of hα-synuclein immunoreactivity. Approximately 50 neurons/animal were analyzed and averaged. Values were calculated as percentage of the mean value in hα-synuclein–devoid cells. (B and C) hα-Synuclein AAV–injected mice were treated with saline (n = 4) or paraquat (n = 5) and sacrificed at 2 days. They also received a DHE injection. (B) Representative confocal images show hα-synuclein–positive neurons (red) containing fluorescent ox-DHE (blue-green-yellow) in the left DMnX. Scale bar: 5 μm. (C) Integrated density of ox-DHE fluorescence within hα-synuclein–immunoreactive neurons in the left DMnX of mice treated with saline (gray bar) or paraquat (red bar). Approximately 50 neurons/animal were analyzed and averaged. Values were calculated as percentage of the mean value in hα-synuclein AAV/saline–injected animals. (D) hα-Synuclein AAV-injected mice were treated with either saline or paraquat and sacrificed at 2 (n ≥ 5/treatment) or 7 (n = 7/treatment) days after treatment. A group of control animals (n = 8, light blue bar) were only injected with saline. The number of Nissl-stained neurons was counted stereologically in the left DMnX. Box and whisker plots show median, upper and lower quartiles, and maximum and minimum as whiskers. *P ≤ 0.05; **P ≤ 0.01; ***P ≤ 0.001, Mann-Whitney U test (A and C) or Kruskal-Wallis followed by Conover-Iman post hoc test (D).