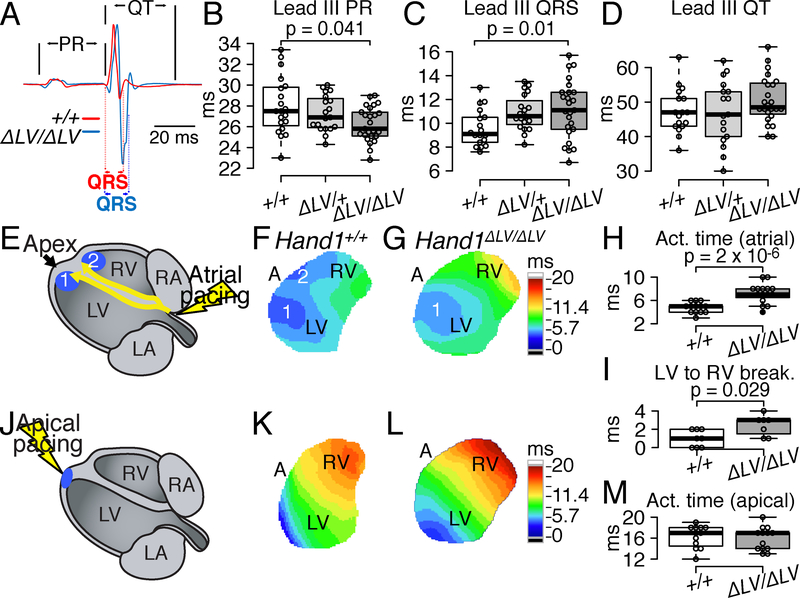
Figure 3. VCS function is abnormal in Hand1ΔLV/ΔLV mutants.
A) Representative lead II ECG tracings show prolonged QRS in Hand1ΔLV/ΔLV mutants (blue) compared to Hand1+/+ controls (red) at P35. B-D) Lead II ECG analyses confirm that PR interval (B) is shortened (p=0.041) and QRS duration (C) is prolonged in Hand1ΔLV/ΔLV mutants compared with Hand1+/+ (p=0.01) and Hand1ΔLV/+ littermates (p=0.021). QT interval (D) is unaltered. Center lines - medians; box limits - 25th and 75th percentiles; whiskers - 1.5X the interquartile range from the box limits. Individual data points are represented by open circles outliers represented by closed circles. n = 18 wild-type, 19 Hand1ΔLV/+, and 25 Hand1ΔLV/ΔLV mutants. E-G) Ventricular epicardial activation mapping in Langendorff-perfused hearts during right atrial pacing at a cycle length of 120 ms. Schematized atrial pacing (E) illustrates sites (blue dots 1 and 2) corresponding to the endocardial insertions of the Purkinje network branches. (F, G) Activation maps obtained from the anterior epicardial surfaces, with color-coded isochronal lines 1 ms apart. Time scales presented in ms, are to the right of the optical maps: dark blue, 0–5.7 ms; light blue to light green, 5.7 to 8.55 ms; green to light yellow 8.55 to 11.4 ms; light yellow to light orange 11.4 to 14.25 ms; light orange to red 14.25 to 17.1 ms; red to dark red 17.1 to 20 ms. H) Differences in epicardial activation times (p=2X10−6) during atrial pacing between Hand1+/+ (white) and Hand1ΔLV/ΔLV (grey) hearts. I) RV epicardial breakthroughs, relative to the LV, in Hand1+/+ (n=8) and Hand1ΔLV/ΔLV (n=7) hearts (p=0.029). J) Schematized apical pacing showing to point of initial epicardial activation (blue). K and L) Isochronal activation maps obtained during direct ventricular pacing at a cycle length of 120 ms in the hearts respectively shown in (F) and (G) time scale identical to that of F and G. M) Epicardial activation times during apical pacing for the same hearts as in (H). p values calculated for B and C employed one-way ANOVA followed by Tukey’s test for post hoc analyses. P values in H and I were calculated using Mann-Whitney Rank Sum test. All sample sizes indicate biological replicates.