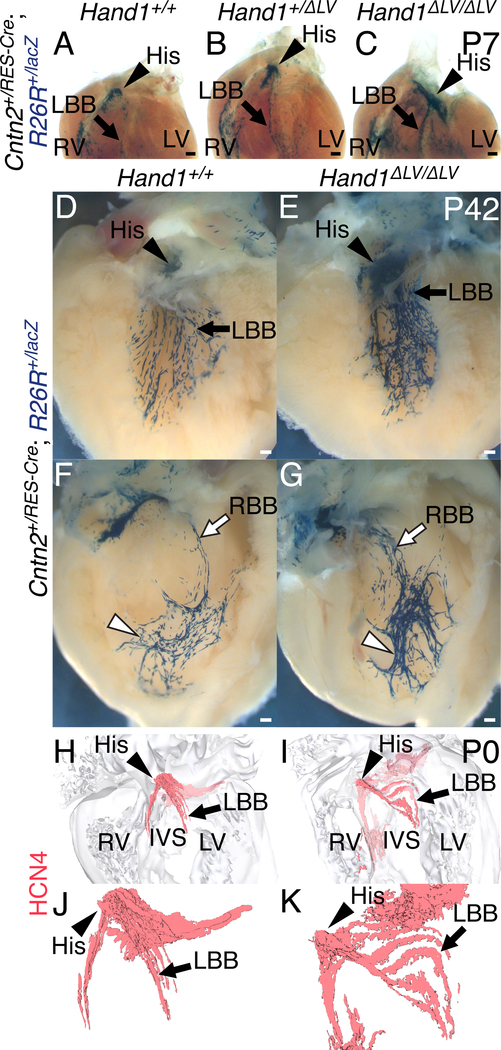
Figure 5. VCS hyperplasia in Hand1ΔLV/ΔLV mutants.
A-C) P7 hearts of Hand1ΔLV/ΔLV mutants bred onto a Cntn2IRES-Cre; R26RlacZ CCS reporter. The atria and great vessels have been removed, and the hearts have been stained in whole mount with X-gal and cleared. Hand1ΔLV/ΔLV;Cntn2+/IRES-Cre;R26R+/lacZ hearts (C; n = 7) displayed an increased number of X-gal-positive His bundle (arrowhead) and left bundle branch (arrow) cells, relative to Hand1+/+;Cntn2+/IRES-Cre;R26R+/lacZ (A) and Hand1+/ΔLV;Cntn2+/IRES-Cre;R26R+/lacZ hearts (B). D-G) P42, X-gal-stained Hand1ΔLV/ΔLV;Cntn2+/IRES-Cre;R26R+/lacZ hearts (E) display a hyperplastic His bundle (arrowhead), and a significantly broader X-gal-positive staining domain overlapping with the LBB (arrow; n = 4/5), than Hand1+/+ controls (D). The peripheral portions of the RBB network (white arrowheads) in Hand1ΔLV/ΔLV;Cntn2+/IRES-Cre;R26R+/lacZ hearts (G) appear more compacted, and the proximal portions (white arrow) more spread out, and with more fascicles than Hand1+/+ controls (F; n = 3/5). Scale bars = 200 μM. H-K) 3D-reconstructions of HCN4 immunohistochemistry (red) upon sections of P0 hearts. Hand1ΔLV/ΔLV mutants (I, K) display abnormally dispersed, hyperplastic His bundles (white arrowheads) and left bundle branches (white arrows) compared with wild-type controls (H, J). Ventral views of the heart showing HCN4-positive cells with (H, I) and without (J, K) the surrounding myocardial cells (gray) are shown. All Scale bars = 200 μM. Sample sizes indicates biological replicates.