Figure 5.
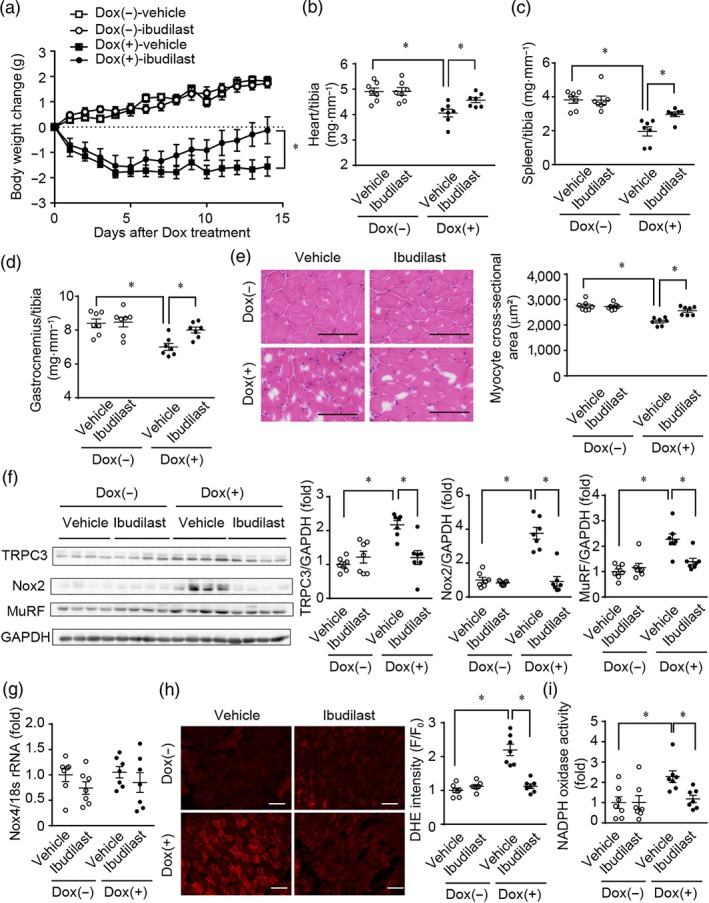
Treatment of mice with ibudilast attenuates doxorubicin‐induced systemic tissue wasting. (a) Reduction of mouse body weight by doxorubicin treatment. C57BL/6J mice were administered doxorubicin (15 mg·kg−1, i.p.). Osmotic pumps including ibudilast (10 mg·kg−1·day−1) or vehicle were implanted intraperitoneally 3 days before doxorubicin administration. (b–d) Tissue weights of the gastrocnemius muscle (b), spleen (c), and heart (d). (e) Representative haematoxylin and eosin staining images (left) and quantitative results of average myocyte cross‐sectional area in mouse gastrocnemius muscles (right). Scale bar: 100 μm. (f) Protein expression of TRPC3, Nox2, and MuRF in mouse gastrocnemius muscles. (g) Expression levels of Nox4 mRNAs in mouse gastrocnemius. (h) Representative dihydroethidium (DHE) fluorescence images (left) and semiquantitative results of average DHE fluorescence intensity in mouse gastrocnemius muscles (right). Scale bar: 100 μm. (i) Quantitative results of average NADPH oxidase activity in mouse gastrocnemius muscles. Data are shown as the mean ± SEM (n = 7). *P < .05, significantly different as indicated; two‐way ANOVA with Tukey's comparison test in (a) and Sidak's comparison test in (b–h)
