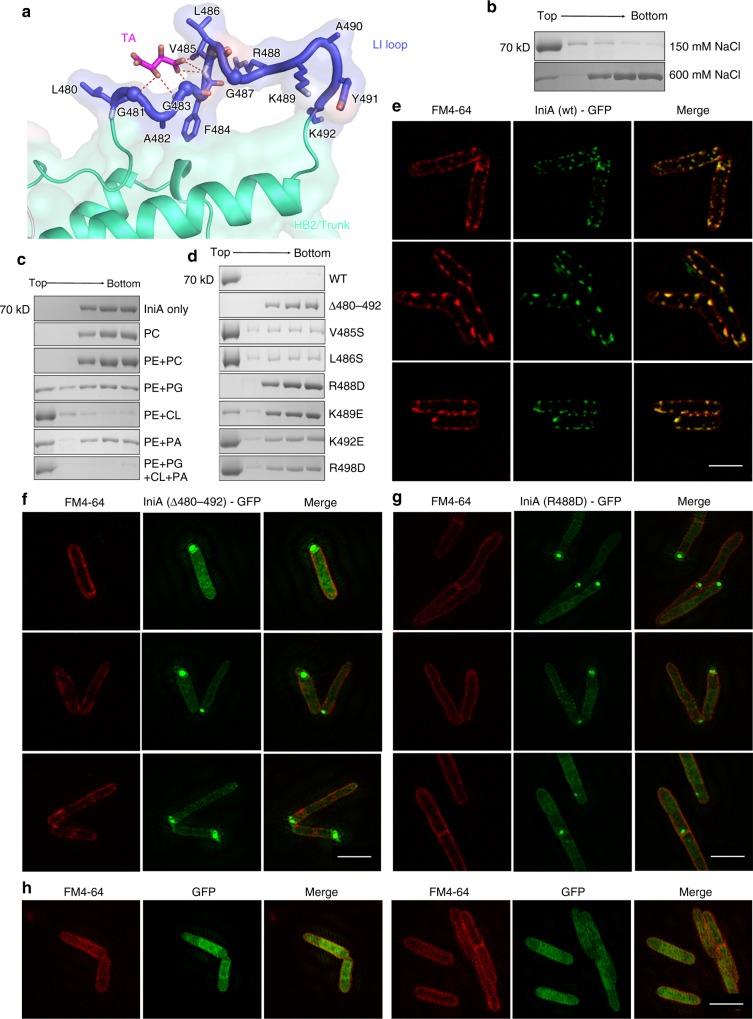
Fig. 3.
LI loop-mediated membrane association. a Residue conformation of the LI loop. Residues are shown as sticks, except that Gly is represented as a sphere. Tartaric acid (TA) interacts with the main chain N atoms in the LI loop (indicated by the dashed lines). b Liposome (E. coli polar lipids containing 78 mol% PE, 12 mol% PG, 6 mol% CL, 4 mol% PA) flotation assay showing the effect of NaCl concentration (150 mM and 600 mM) on IniA membrane association. c As shown in (b), but testing the effect of different lipids (100 mol% PC; 50 mol% PE, 50 mol% PC; 80 mol% PE, 20 mol% PG; 80 mol% PE, 20 mol% CL; 80 mol% PE, 20 mol%PA; 78 mol% PE, 12 mol% PG, 6 mol% CL, 4 mol% PA) for recruiting IniA. d As shown in (b), but with mutants at the LI loop. Δ480–492, L480-K492 was replaced by the GGGGSGGGGS linker. e IniA(wt)-GFP fusion protein was expressed in M. smegmatis, and their localization determined by GFP (green) and compared with that of FM4–64 (red) inserted in the membrane by confocal microscopy. Scale bars, 2 µm. f–h As shown in (e), the mutants IniA(Δ480–492)-GFP (f) and IniA(R488D)-GFP (g) and the control GFP (h) were also performed. Scale bars, 2 µm. The source data of Fig. 3b–d are provided in the Source Data file