Figure 1.
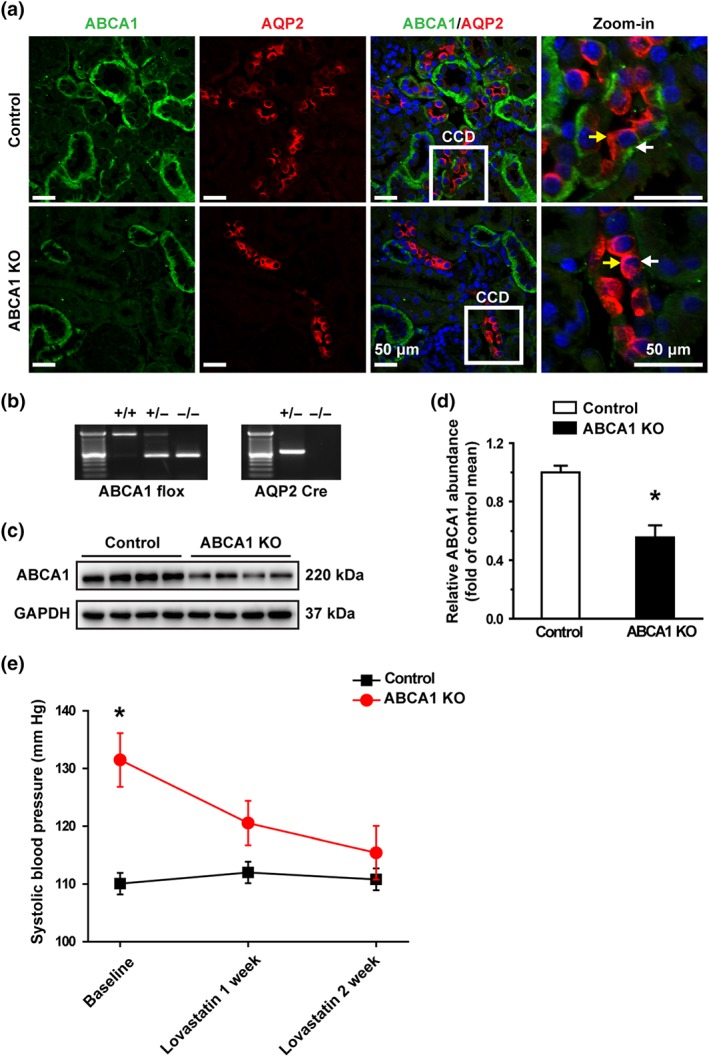
Lovastatin corrects hypertension caused by loss of ABCA1 function. (a) Confocal microscopy images of ABCA1 (green) in control and ABCA1 KO mice. The principal cells in CCD were labelled with an anti‐AQP2 antibody shown in red (also applied to other figures). ABCA1 was expressed in the basolateral membrane of the kidney cortex epithelial cells; AQP‐2 was expressed in the apical membrane of the CCD principal cells. Each experiment was repeated three times in each mouse. The images represent data from six mice, showing consistent results. Yellow arrowheads indicate apical membrane of the cell; white arrowheads indicate the basolateral membrane of the cell. Scale bars: 50 μm. (b) Genotyping analysis of 4‐week‐old mice. (c) Western blot of kidney cortex lysates from control and ABCA1 KO mice using antibodies against either ABCA1 or GAPDH as a loading control. (d) Summary data of western blots showing ABCA1 expression in kidney cortex from control and ABCA1 KO mice; n = 8 in each group. *P < .05, significantly different from control; Student's two‐tailed t‐test. (e) SBP from ABCA1 KO mice (n = 9 ) was significantly increased, compared with control mice (n = 7), while lovastatin attenuated the elevated SBP. *P < .05, significantly different from control; two‐way ANOVA followed by Bonferroni's post hoc test
