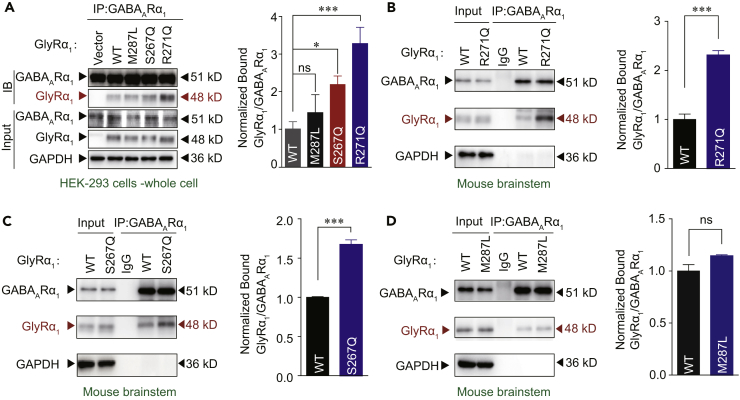
Figure 3.
Identification of Interaction between GABAAR and Hyperekplexic Mutant GlyRs
(A) GlyRα1 was purified using GABAAR α1 antibodies in HEK-293 cells co-expressing GABAARs (α1β2γ2) and WT/mutant α1 GlyRs, and the co-precipitating proteins were detected by immunoblotting. Inputs are immunoblots of the same protein in cell lysates before Co-IP. Quantification of WT and mutant GlyR α1 binding to GABAAR α1 subunits (n = 3). The data were normalized to the WT group.
(B and C) Endogenous brainstem GlyRα1 of WT and GlyRα1 R271Q (B) or S267Q (C) KI mice was purified using GABAAR α1 antibodies, and the co-precipitating proteins were detected by immunoblotting. Inputs are immunoblots of the same protein in tissue lysates before Co-IP. Quantification of WT and R271Q (B) or S267Q (C) mutant GlyRα1 binding to GABAARα1 (n = 3 mice).
(D) Endogenous brainstem GlyRα1 of WT and GlyRα1 M287L KI mice was purified using GABAAR α1 antibodies, and the co-precipitating proteins were detected by immunoblotting. Inputs are immunoblots of the same protein in tissue lysates before Co-IP. Quantification of WT and M287L mutant GlyRα1 binding to GABAARα1 (n = 3 mice). The data were normalized to the WT group.
Data are represented as mean ± SEM. *p < 0.05, ***p < 0.001 based on unpaired t tests; ns, not significant (p > 0.05).