Figure 4.
Molecular Dynamic Simulation, Mutagenesis, and Correlation Analysis
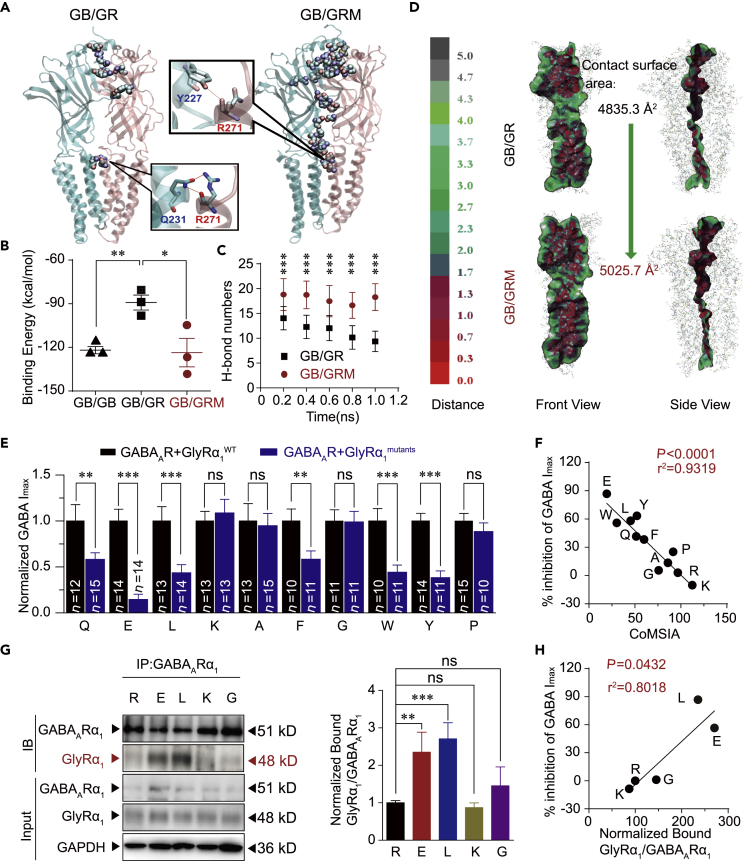
(A) Overview of residues forming H-bond between GB chain and GR chain in the GB/GR and GB/GRM complexes at the end of the simulation. GB chain and residue labels are colored in cyan. GR chain and residue labels are colored in pink. H-bonds are shown by the red dashed line.
(B) Binding energy (kcal/mol) between subunits in various composing form of dimers.
(C) Number of H-bonds formed between GB chain and GR chain in the GB/GR and GB/GRM complexes. The data are shown as averages of each 200 ps. Data are represented as mean ± SD.
(D) VDW contact surface between GB chain and GR chain in the GB/GR and GB/GRM complexes. Proteins are displayed in lines. Contact surfaces were mapped and colored according to the distances between two chains.
(E) Average values of GABA Imax induced by 1 mM GABA in HEK-293 cells co-expressing GABAARs and various R271 site mutant GlyR α1 subunits. All data were normalized to their respective controls (WT group).
(F) Correlation analysis of CoMSIA values of various amino acids at 271 and the percentage inhibition of GABA Imax.
(G) GlyRα1 was purified using GABAAR α1 antibodies in HEK-293 cells co-expressing GABAARs (α1β2γ2) and GlyRα1 carrying various R271 mutations, and the co-precipitating proteins were detected by immunoblotting. Inputs are immunoblots of the same protein in cell lysates before Co-IP. Quantification of WT and R271 mutant GlyRα1 binding to GABAAR α1 (n = 3). Data were normalized to the WT group.
(H) Correlation analysis of the percentage decrease in GABA Imax and amount of R271 mutant α1 GlyRs co-immunoprecipitated with GABAARs.
All digits within the columns represent numbers of cells measured. Data are represented as mean ± SEM. **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001 based on unpaired t tests; ns, not significant (p > 0.05).