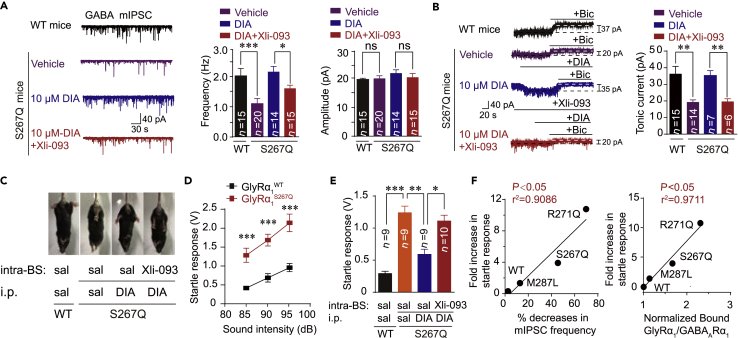
Figure 7.
DIA Rescues Dysfunction of Pre- and Extra-synaptic α5-Containing GABAARs and Exaggerated Startle Responses in Hyperekplexic Mutant Mice
(A) Trace records, average frequency, and amplitude of GABAergic mIPSCs in brainstem hypoglossal nucleus slices from WT and GlyR α1 S267Q mutant mice with or without diazepam (10 μM) and/or Xli-093 (1 μM) pre-incubation.
(B) Trace records and average values of bicuculline-sensitive tonic currents (BSTC) in brainstem hypoglossal nucleus slices from WT and GlyR α1 S267Q mutant mice with or without diazepam (10 μM) and/or Xli-093 (1 μM) pre-incubation.
(C) Hind feet clenching behavior in GlyRα1S267Q mutant mice and effect of DIA (i.p. 10 mg/kg) and Xli-093 (intra-brainstem hypoglossal nucleus injection, 5 μg) on this behavior.
(D) Average values of startle responses induced by white noise at 85, 90, and 95 dB in WT (n = 8) and GlyRα1S267Q (n = 8) mice.
(E) Average values of startle response activated by white noise at 85 dB in WT and GlyRα1S267Q mutant mice with or without diazepam (i.p. 10 mg/kg) and/or Xli-093 (intra-brainstem hypoglossal nucleus injection, 5 μg) treatments.
(F) Correlation analysis of fold increases in startle response, percentage decreases in mIPSC frequency, and amount of mutant α1 GlyRs co-immunoprecipitated with GABAARs in hyperekplexic mutant mice.
All digits within the columns represent numbers of cells or mice measured. Data are represented as mean ± SEM. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001 based on unpaired t tests; ns, not significant (p > 0.05).