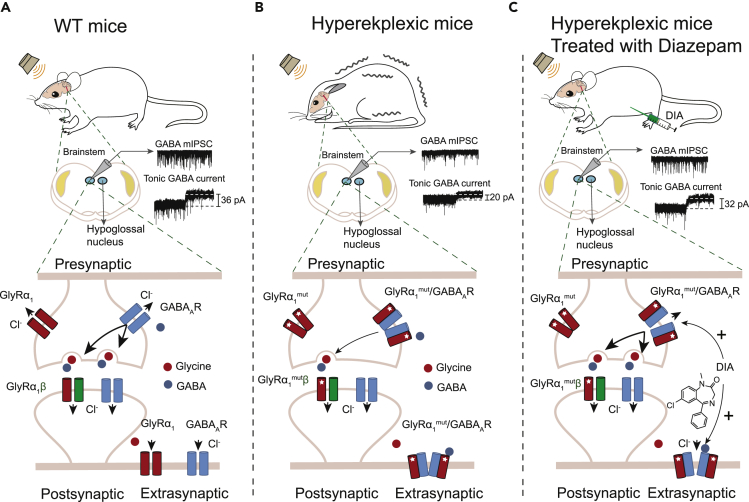
Figure 8.
Schematic of Mechanisms in which Hyperekplexic Mutant GlyRs Disrupt Inhibitory Neurotransmission by Interacting with Pre- and Extra-synaptic GABAARs
(A) Under normal conditions, presynaptic GABAARs facilitate GABA release from GABAergic neuron terminals, activating postsynaptic GABAARs to inhibit neurons in the brainstem hypoglossal nucleus. The extra-synaptic GABAARs mediate the chronic inhibition of postsynaptic neurons in the brainstem hypoglossal nucleus.
(B) In hyperekplexia disease, the mutant GlyRα1 binds to pre- and extra-synaptic GABAARs and, therefore, reduce GABA release and the chronic inhibition. The postsynaptic GlyRβ subunits prevent the mutant GlyRα1 from binding to the GABAARs.
(C) DIA exerts its therapeutic effect by allosterically potentiating pre- and extra-synaptic α5-containing GABAARs in the brainstem hypoglossal nucleus.