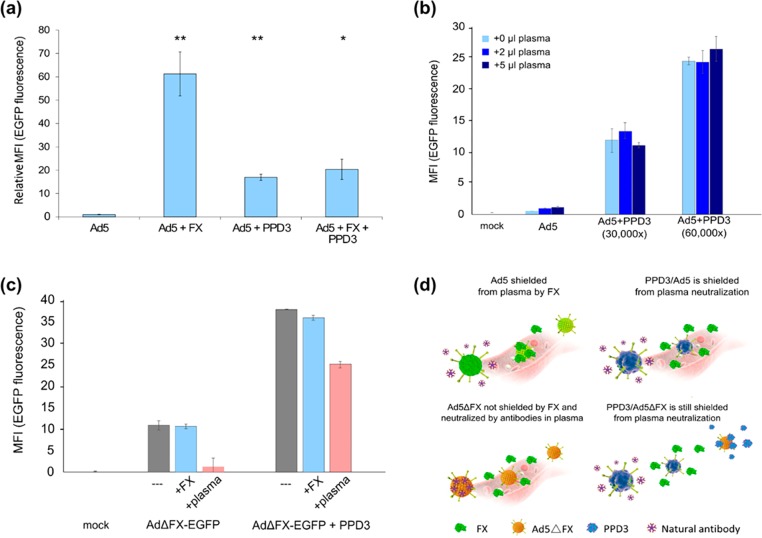
Figure 3.
PPD3/Ad5 complexes exhibit increased transduction efficiency in human plasma and PPD3 protected FX-binding ablated capsids from neutralization by the IgM/complement pathway. (a) PPD3/Ad5 complexes were formed and SKOV-3 cells transduced (1000 pMOI) in the presence or absence of FX at its physiological concentration (8 μg/mL). While FX was expectedly able to significantly increase transduction of SKOV-3 cells, the transduction by PPD3/Ad5 complexes was not enhanced by FX, suggesting that PPD3/Ad5 complexes may not be able to bind FX. (b) PPD3/Ad5 complexes exhibited increased transduction of largely refractory SKOV-3 cells in the presence of human plasma of an Ad-naïve donor (1000 pMOI). (c) FX is known to shield Ad5 particles from attack by natural IgM antibodies and complement. A FX-binding ablated Ad5 vector, a preferable tool for gene transfer and oncolysis due to its significantly reduced hepatotropism, did not show enhanced transduction on SKOV-3 cells (1000 pMOI) but was expectedly neutralized after addition of 5 μL of plasma from an Ad-naïve donor. PPD3/Ad complexes at a molar excess of 30 000-times were largely resistant to neutralization, indicating that PPD3 can replace FX as a protective shield against IgM/complement. (d) Comparison of uncoated Ad5, PPD3/Ad5, Ad5ΔFX, and PPD3/Ad5ΔFX for their FX binding and subsequent neutralizing antibody binding. ∗ represents p-value ≤ 0.05, ∗∗ represents p-value ≤ 0.01.