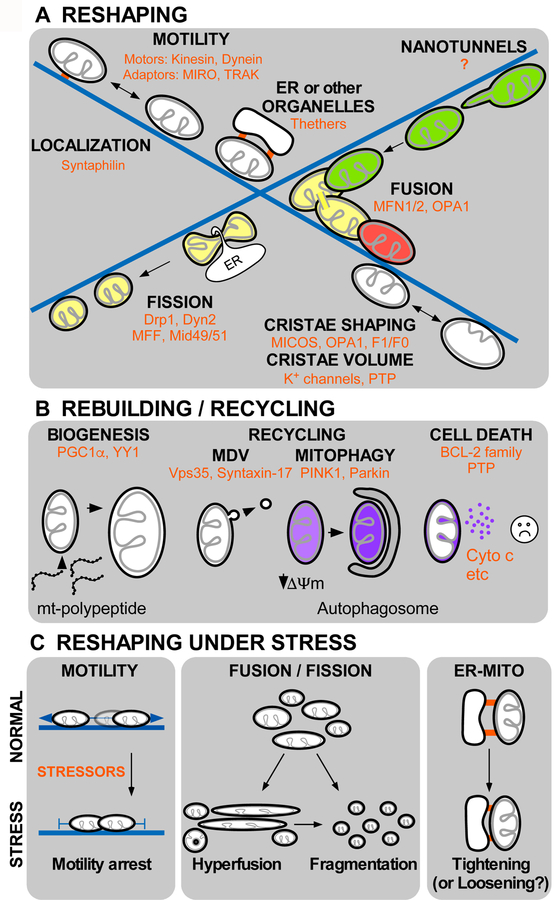
Figure 2. Components of mitochondrial dynamics and their response to stress:
A. Reshaping, localization and motility of mitochondria (depicted by black OMM and gray IMM) along the microtubules (blue) supported by molecular motors (Kinesin and Dynein) and adaptors (MIRO and TRAK) facilitates the inter-organelle communication and physical tethering with the ER or other organelles. Mitochondrial fusion (green and red organelles merge to result yellow post-fusion content) occurs in association to microtubules and mediated by GTPase proteins located at the OMM (MFN1/2) and IMM (OPA1). Fission of mitochondria is also supported by association with the ER, and triggered by DRP1 and Dynamin2 GTPases. Recently described dynamic processes are mitochondrial nanotunnel formation that also depends on interaction with microtubules, intra-mitochondrial dynamics directed by MICOS (mitochondrial contact site and cristae organizing system), OPA1 and F1/F0 (ATP synthase) and matrix volume changes, depending on IMM K+ channels and the Permeability Transition Pore (PTP). B. Rebuilding and recycling processes, mitochondrial biogenesis involves expression of organelle-targeted proteins upon activation of transcriptional factors PGC1-α and YY1, and phospholipids biosynthesis. Recycling of mitochondria can be mediated by mitochondria derived vesicles (MDVs) regulated by Vps35, Syntaxin-17, and mitophagy, driven by PINK1 and Parkin. Mitochondria host cell death signaling pathways that control cytochrome c release to decide on cell survival or removal C. Mitochondrial reshaping under stress. Diverse stressors (red) trigger adaptive responses in mitochondrial reshaping processes. Stressors commonly cause mitochondrial motility arrest, hyperelongation and donut formation or total fragmentation. Under stress, ER-mitochondria contacts usually become tighter but loosening has also been documented.