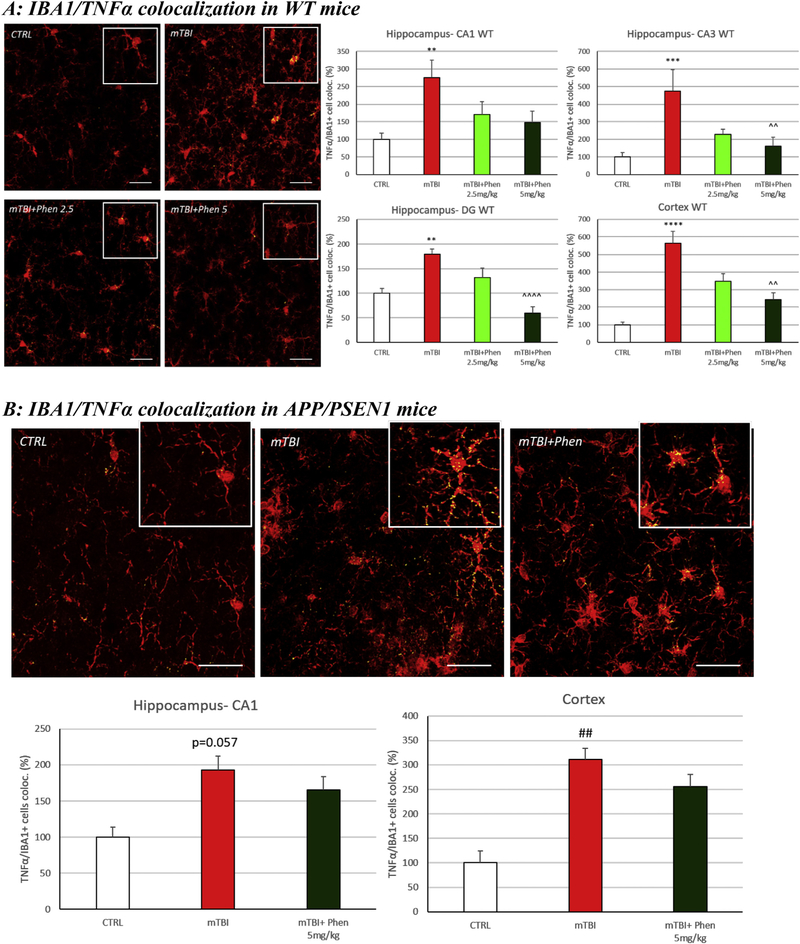
Fig. 4.
Phen inhibits mTBI-induced TNF-α generation within activated microglial in WT and APP/PSEN1 mice. mTBI induced an elevation in immunoreactivity for the pro-inflammatory cytokine TNF-α within IBA1+ cells across all analyzed brain areas in WT animals (Fig. 4A) and in the cortex of APP/PSEN1 mice (Fig. 4B), as evaluated by TNF-α/Iba1 co-localization. By contrast, mTBI Phen-treated mTBI mice had values no different from the sham (CTRL) group. Administration of Phen (2.5 and 5 mg/kg, BID) reduced the levels of IBA1/TNF-α IR co-localization volume across all hippocampal and cortical areas in WT mTBI-challenged mice, as compared to the mTBI vehicle group. Representative confocal images showing co-localized elements (yellow) in IBA1 (red) positive cells in cortex. Percentage of co-localization of TNF-α IR in IBA1 positive cells. **p < .01, ***p < .001, ****p < .0001 vs. CTRL by Tukey’s post hoc test; ^^p < .01, ^^^^p < .0001 vs. mTBI by Tukey’s post hoc test. ##p < .01 vs. CTRL by Mann-Whitney rank test. Data shown as mean ± S.E.M. Scale bar = 30 μm.