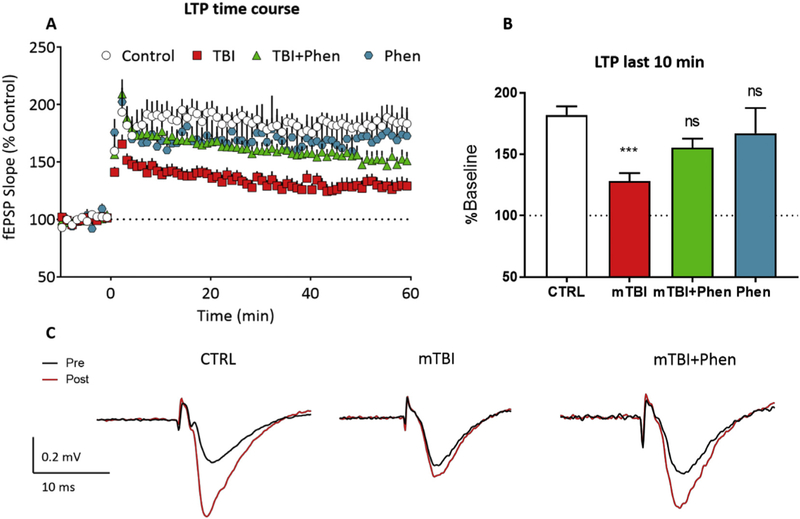
Fig. 6.
Phen mitigates mTBI-induced deficits in LTP in WT mice.
(A) Time course of the mTBI-induced impairment in LTP (initiated by HFS at time = 0 on the x-axis) across the 60 min time course. The fEPSP slope is expressed as a % of the control baseline, collected prior to HFS. (B) LTP magnitude, evaluated over the last 10 min of recording in each of the groups shown in A. (C) Representative averaged traces of a control slice, a slice from a mTBI mouse, a slice from a mTBI+Phen 5 mg/kg mouse, and a slice from control mouse treated with 5 mg/kg Phen showing the mitigating effect of Phen treatment on the mTBI-induced LTP impairment. Traces are averaged from the period immediately prior to (pre) and 60min following (post) high-frequency stimulation. LTP in mTBI-Veh mice was significantly decreased as compared with the sham (CTRL) group. Note that treatment of mTBI-challenged mice with Phen (5 mg/kg, BID) mitigated the LTP impairment, and that the mTBI Phen group did not statistically differ from sham (CTRL) animals. Data shown as mean ± S.E.M. ***p < .001, one-way ANOVA (F (3,49) = 6.053), and Tukey’s post-hoc test.