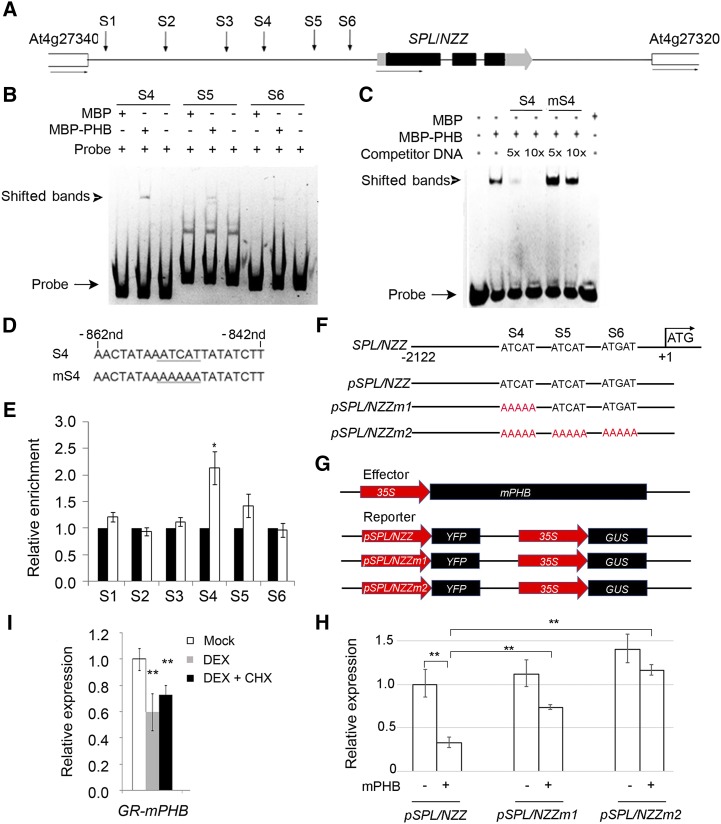
Figure 4.
Binding of PHB in the promoter of SPL/NZZ. A, Diagram of SPL/NZZ genomic regions showing the positions of putative binding sites (S1–S6, indicated by arrows). The gray and black boxes indicate the untranslated region and exon regions, respectively, while the lines indicate intergenic regions and introns. B, EMSA showing the binding affinity of the putative sites of SPL/NZZ promoter regions by PHB. The positions of PHB-DNA complexes are marked by shifted bands. C, Competitor DNA-binding assay showing the binding affinity of the S4 site of the SPL/NZZ promoter regions by PHB. D, Sequences of the S4 site and its competitor DNA. E, ChIP assays showing PHB binding to the SPL/NZZ promoter. F, DNA sequences of the wild-type SPL/NZZ promoter and mutant SPL/NZZ promoters. G, Structure of the SPL/NZZ promoter-driven YFP reporter gene. The SPL/NZZ promoter, 35S promoter, YFP, GUS, and PHB genes are indicated. H, Relative reporter (YFP) expression in plants with different SPL/NZZ promoters. N. benthamiana leaves were transfected with the reporters (pSPL/NZZ, pSPL/NZZm1, and pSPL/NZZm2) and the effector (mPHB). I, RT-qPCR showing relative expression of SPL/NZZ in p35S::GR-mPHB lines treated with DEX and DEX + CHX solutions. Three biological replicates were analyzed. Error bars indicate the sd, while asterisks show significant differences at the 0.05 (*) and 0.01 (**) levels in Student’s t test.