Figure 5.
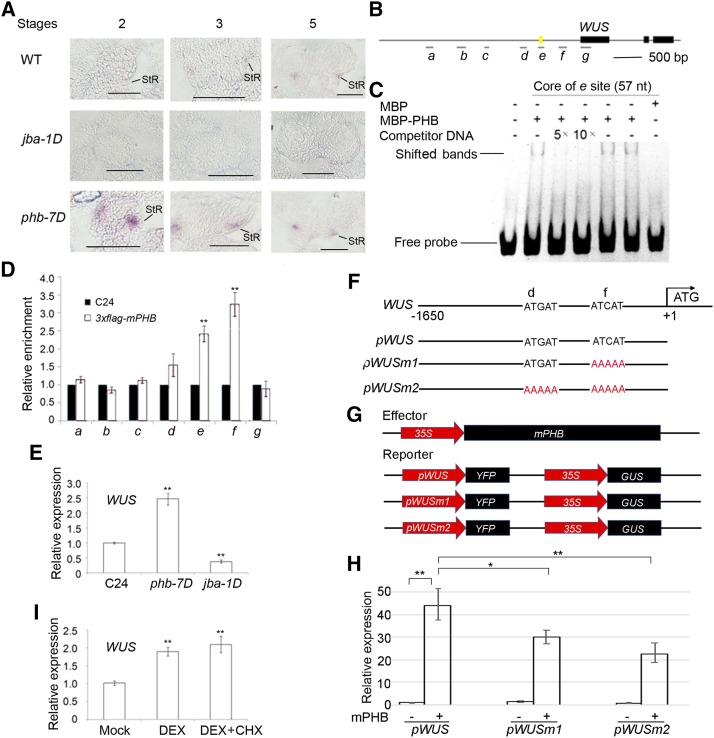
Binding of PHB in the promoter of WUS. A, In situ hybridization showing the expression patterns of WUS in developing anthers of jba-1D and phb-7D mutants. StR, Stomium regions; WT, wild type. Bars = 50 μm. B, Putative binding sites of PHB in WUS. Letters a, b, c, d, e, f, and g represent seven putative binding sites in WUS. The yellow mark indicates a 57-bp regulatory region (−655 to −712 bp) conferring WUS transcription in the shoot apical meristem stem cell niche. C, EMSA showing the binding affinity of the putative sites of WUS promoter regions by PHB. The positions of PHB-DNA complexes are marked by shifted bands. D, ChIP assays showing PHB binding to the WUS promoter. E, RT-qPCR showing relative expression of WUS in phb-7D and jba-1D. F, DNA sequences of the wild-type WUS promoter and mutant WUS promoters with mutations in different binding sites. G, Schematic diagram of the reporter (pWUS, pWUSm1, and pWUSm2) and effector (mPHB) constructs. H, RT-qPCR showing relative expression of YFP measured after transient transformation of the reporter (pWUS, pWUSm1, and pWUSm2) and effector (mPHB) constructs in N. benthamiana leaves. I, RT-qPCR showing relative expression of WUS in p35S::GR-mPHB lines treated with DEX and DEX + CHX solutions. Three biological replicates were analyzed. Error bars indicate the sd, while asterisks show significant differences at the 0.05 (*) and 0.01 (**) levels in Student’s t test.