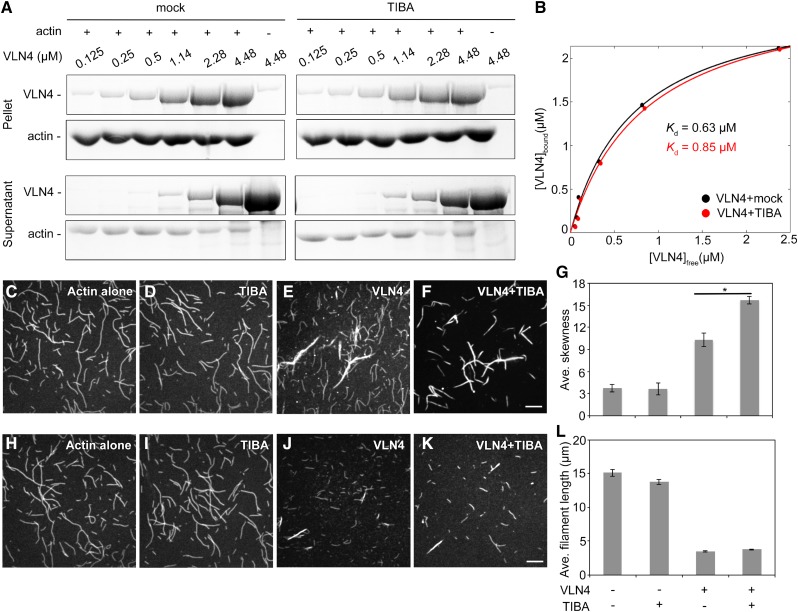
Figure 6.
TIBA enhances the bundling activity of VLN4. A and B, A high-speed cosedimentation assay was used to examine the effect of TIBA on VLN4 binding to F-actin. Increasing concentrations of VLN4 were cosedimented with F-actin (3 µm). The supernatants and pellets obtained were subjected to SDS-PAGE and Coomassie stained. B, The experiments in A were repeated three times. After gel quantification, the concentration of bound VLN4 was plotted against the concentration of free VLN4 and fitted with a hyperbolic function. C to F, The effect of TIBA on VLN4-induced actin bundle formation. Prepolymerized actin (Oregon green-labeled, 3 µm) alone (C), with 500 µm TIBA (D), or 200 nm VLN4 in the absence (E) or presence (F) of 500 µm TIBA. EGTA (2 mm) was added in each reaction mix. Bar = 10 µm (F). G, Skewness analyses were performed on images shown in C to F. Values given are means ± se (n = 50 images for each treatment; *P < 0.05; t test). (H to K, TIBA does not affect the severing activity of VLN4. Prepolymerized actin (Oregon green-labeled, 3 µm) alone (H), with 500 µm TIBA (I), or 150 nm VLN4 in the absence (J) or presence (K) of 500 µm TIBA. All reactions were supplemented with 200 µm free Ca2+. Bar = 10 µm (K). L, Average filament lengths were measured on images shown in H to K. Values given are means ± se (n > 300 filaments for each treatment).