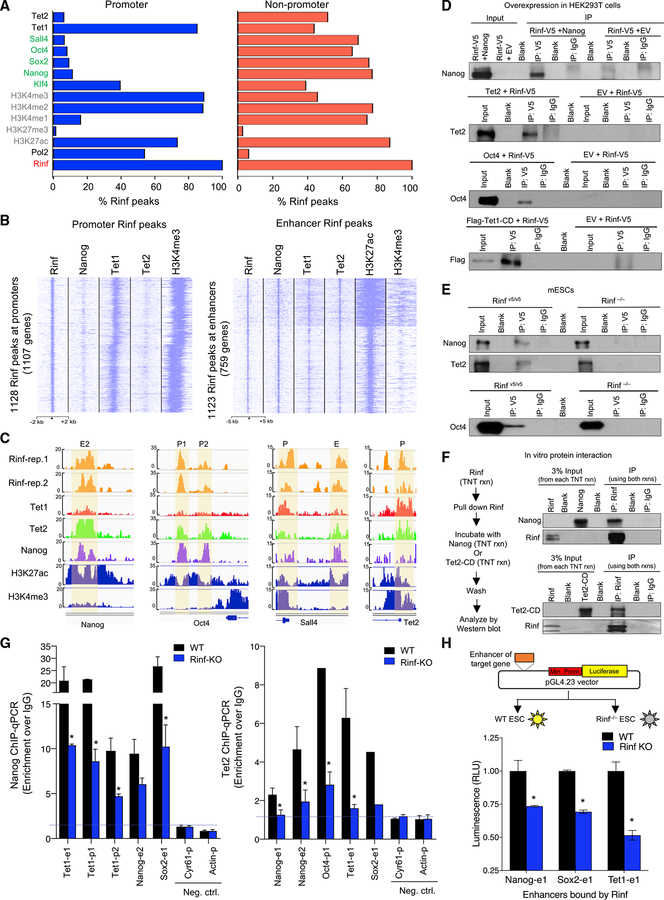
Figure 2. Co-occupancy of Rinf with Pluripotency Factors and Tet Enzymes at Gene Regulatory Regions.
(A) Overlapping analysis of Rinf peaks (from this study) with those of pluripotency factors, Tet enzymes, and activating/repressive histone marks (from previous studies, see STAR Methods). Data presented as % of Rinf peaks overlapping with each of the factors.
(B) Enrichment of Rinf peaks at ChIP-seq signals of Nanog, Tet1, and Tet2 at promoters (±2 kb of TSS and H3K4me3 positive, left) and enhancers (H3K27ac positive and H3K4me3 low, right).
(C) Enrichment of ChIP-seq signals showing co-occupancy of Rinf, pluripotency factors, and Tet enzymes at selected pluripotency and Tet genes. H3K27ac and H3K4me3 tracks are used as reference to depict enhancers and promoters (±2 kb of TSS).
(D) Co-immunoprecipitation of exogenously expressed V5-tagged Rinf with Nanog, Oct4, Tet1 catalytic domain (Tet1-CD), and Tet2 in HEK293T cells using anti-V5 antibody.
(E) Co-immunoprecipitation of endogenous Rinf with Nanog, Oct4, and Tet2 in mouse ESCs using anti-V5 antibody. Rinf−/− ESCs are used as negative control.
(F) Co-immunoprecipitation of in vitro transcribed and translated Rinf, Nanog, and Tet2 catalytic domain (Tet2-CD) from rabbit reticulocyte lysate.
(G) Enrichment of Nanog and Tet2 at regulatory elements of indicated genes quantified by ChIP-qPCR in wild-type and Rinf−/− ESCs (data normalized to IgG). Actin and Cyr61 are used as negative controls.
(H) Schematic of dual luciferase reporter assay applied to test enhancers targeted by Rinf (top). Transcriptional activity is presented as relative luminescence unit (RLU), which is normalized to the luminescence from cells that express the empty vector only (bottom).
Data presented as mean ± SEM. *Statistically significant (p < 0.05). E, enhancer; p, promoter (see also Figure S2).