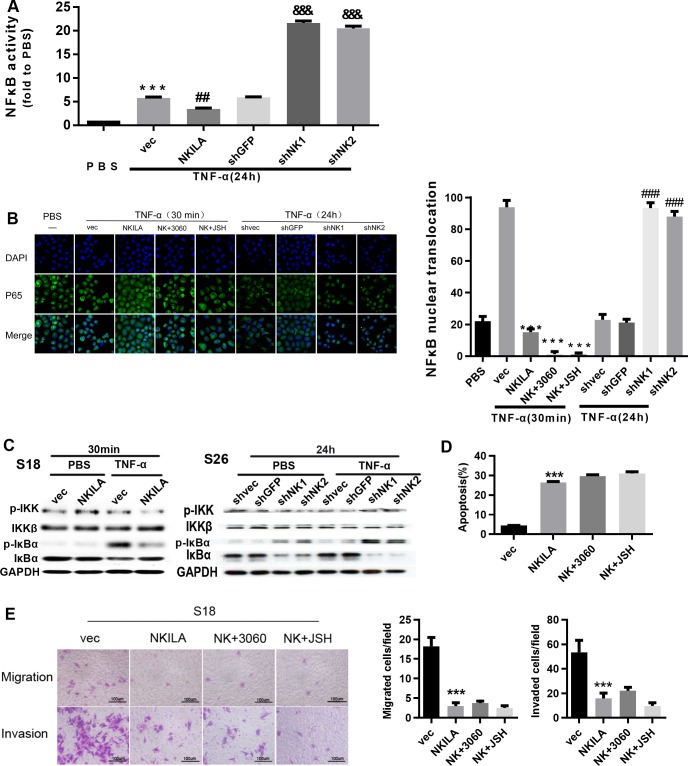
Fig 6. NKILA inhibits the activation of NF-κB by repressing IκB phosphorylation.
(A) Luciferase reporter assay for detection of NF-κB activity in S26 cells treated with TNF-α (mean ± SD, n = 3, &&&, P < 0.001 versus shGFP; ##, P < 0.01 versus vec; ***, P < 0.001 versus PBS). (B) Immunofluorescence confocal microscopy for detection of P65 nuclear translocation in S26 cells with overexpression or depletion of NKILA treated with TNF-α(mean ± SD, n = 3,***, p < 0.001 versus vec, ###, P < 0.001 versus shvec).(C) Total and phosphorylated IKK and IκBα assayed by Western blotting in S26 or S18 cells. (D) Annexin-V/PI staining for detection of apoptosis in S18 cells stably expressing NKILA (48 h after seeding). (mean ± SD, n = 3, ***, P < 0.001 versus vec; 3060:10 mM; JSH:5 mM). (E) Migration and invasion in S18 cells with stably overexpression or depletion of NKILA, assayed by Boyden Chamber assay (16h for migration and 22 h for invasion after seeding, respectively) (mean ± SD, n = 3, ***, P < 0.001 versus S18 vec).