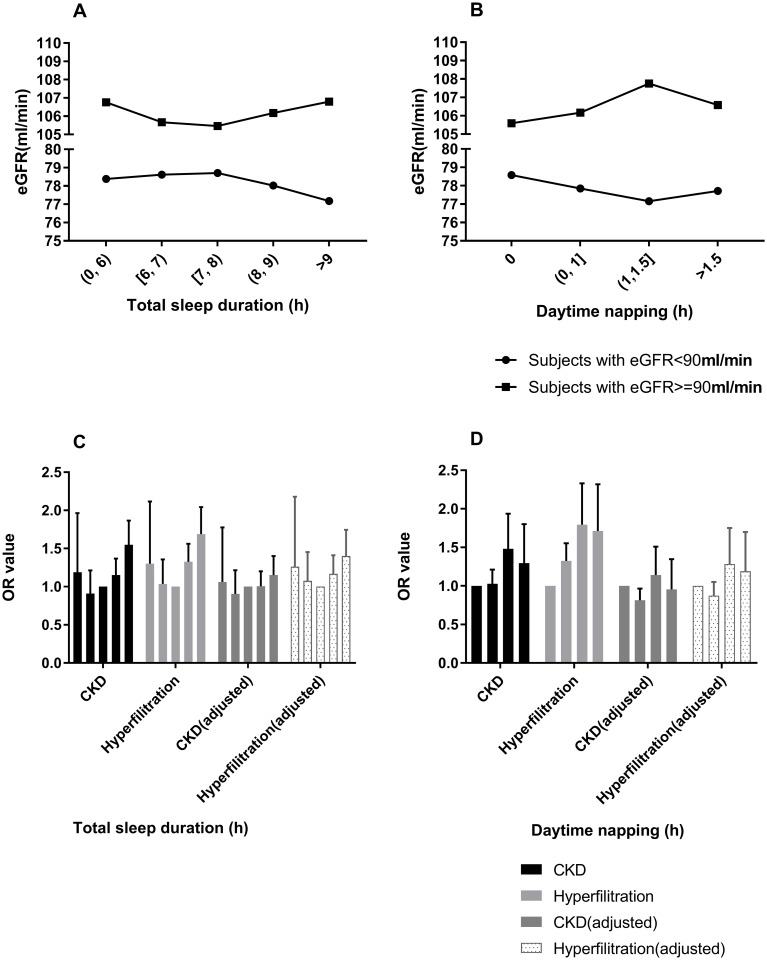
Fig 2. The association between sleep duration and eGFR.
(A) The association between mean eGFR values and total sleep duration among subjects with <90 ml/min and ≥90 ml/min eGFR. (B) The association between mean eGFR values and daytime napping duration among subjects with <90 ml/min and ≥90 ml/min of eGFR. (C and D) Risks for hyperfiltration among subjects with ≥90 ml/min eGFR and risks for CKD among subjects with <90 ml/min eGFR, according to total sleep duration or daytime napping duration. The adjusted covariates included age, sex, BMI, HC, WC, alcohol consumption and smoking habits, physical exercise, TG, TC, HDL, LDL, GGT, blood glucose and blood pressure. CKD was defined as eGFR <60 ml/min, and hyperfiltration was defined as eGFR ≥135 ml/min.