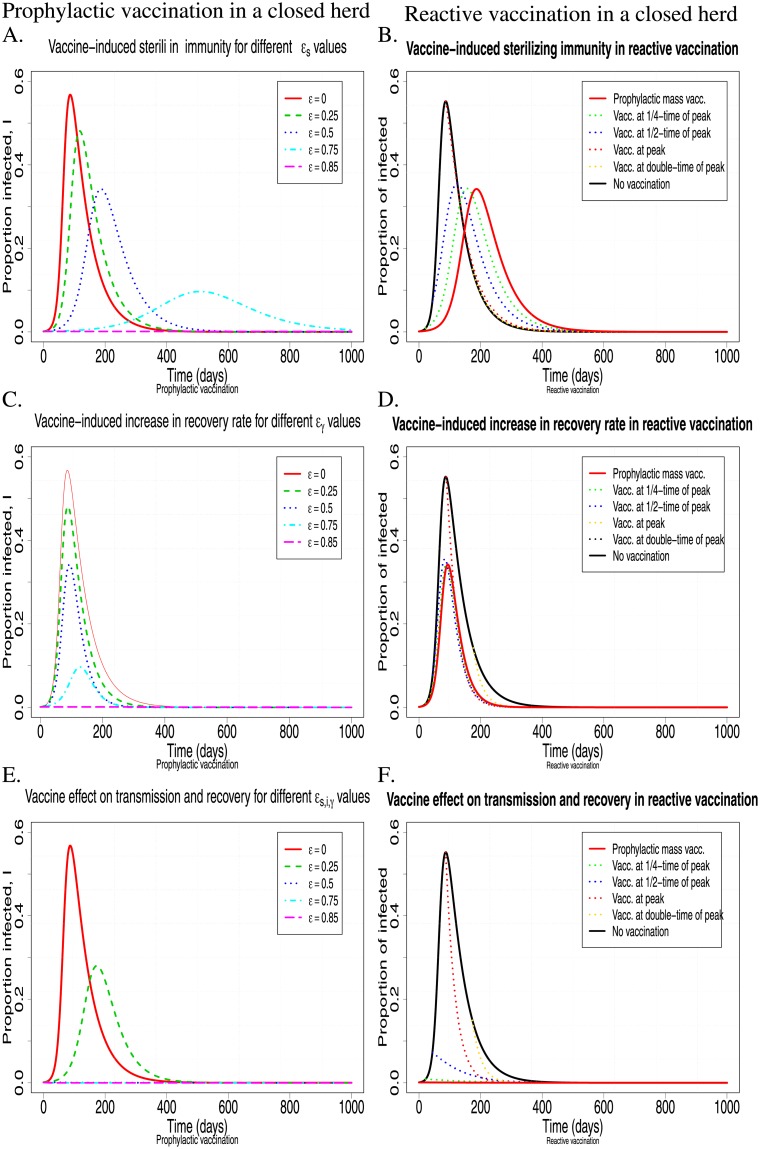
Fig 5. The effect of fully effective mass vaccination (i.e. p = 1 at the time of vaccination) with vaccines of different properties on the infection dynamics in the case of prophylactic (left column) and reactive (right column) vaccination in a closed herd.
Profiles of different colours correspond to different ϵ = ϵs,i,γ values on the infection dynamics (left column; see caption in Fig 4), or different times when vaccination is applied (right column; see caption in Fig 6). A.-B. The vaccine only affects host susceptibility, i.e. sterilizing immunity, but no effect on infectivity or recovery (see Eqs (7) and (10)); C.-D. The vaccine only speeds up recovery, but offers no protection from infection and no reduction in infectivity (see Eqs (9) and (10)); E.-F. The vaccine equally affects host susceptibility, infectivity and recovery rate (see Eqs (7)–(9) and (10)). Here βNN = 0.12, γN = 0.01785, p = 1, d = 0.001, μ = λN,V = 0, and the initial conditions are SV (0) = 0.999, IV (0) = 0.001 (left column) and SN (0) = 0.999, IN (0) = 0.001 (right column).