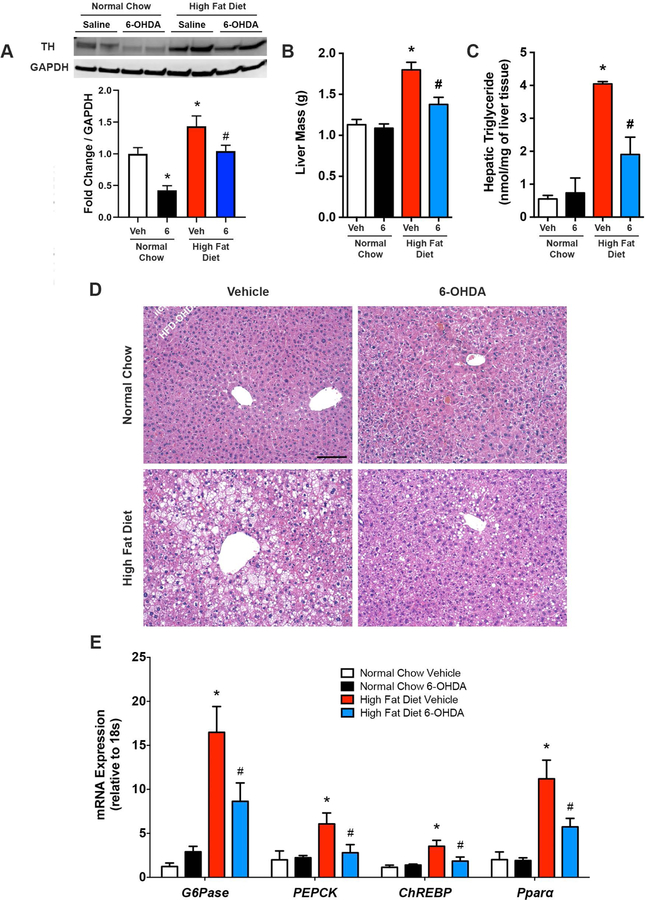
Figure 2. Pharmacological removal of sympathetic nerve activity reduces hepatic steatosis during diet-induced obesity.
6-hydroxydopamine (6) to ablate peripheral sympathetic nerves, or vehicle control (Veh), was administered (i.p.) once in high fat diet and normal chow fed mice and animals were sacrificed 3 days later. (A) Representative western blot and quantitative summary of liver tyrosine hydroxylase (TH) protein expression (n=4–8). (B) Liver mass (n=7–8). (C) Hepatic triglyceride content (n=4–7). (D) Representative liver hematoxylin and eosin staining. Scale bar=100 μm. (E) mRNA expression of liver gluconeogenesis and de novo lipogenesis markers (n-7–8). Two-way ANOVA with Tukey’s post-hoc test for all. *p<0.05 vs. normal chow, #p<0.05 vs. high fat diet vehicle.