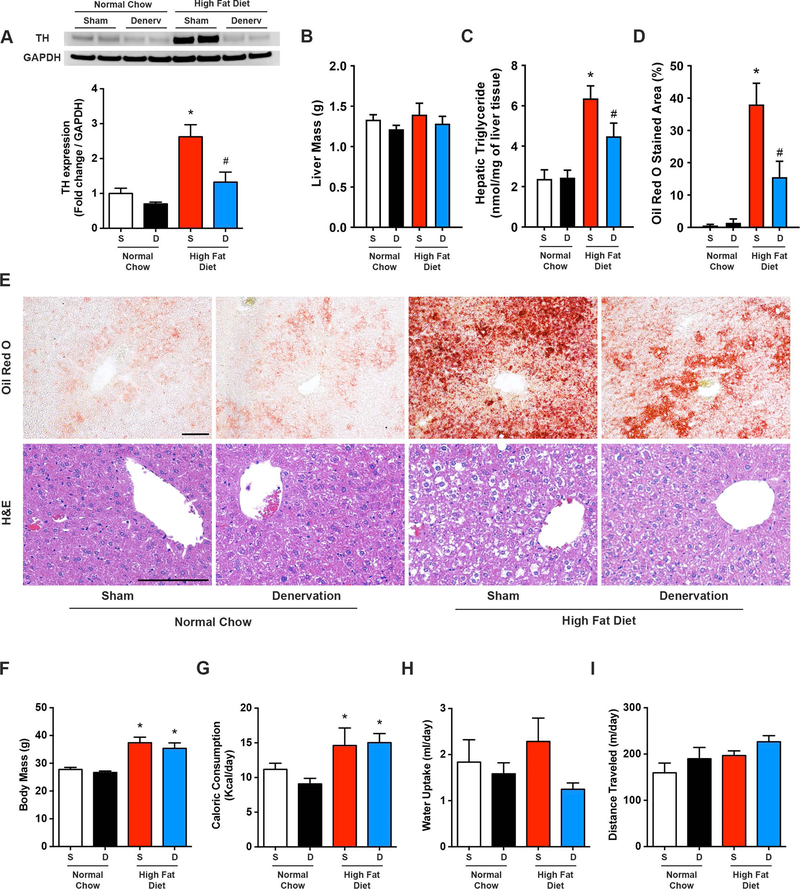
Figure 4. Hepatic denervation reduces diet-induced hepatic steatosis.
High fat diet and normal chow mice underwent selective hepatic denervation (D) or sham (S) surgery and were sacrificed 7 days later. (A) Representative western blot and quantitative summary of liver tyrosine hydroxylase (TH) protein expression (n=4–6). (B) Hepatic triglyceride content (n=4–8). (C) Liver Oil Red O stained area (n=3–4). (D) Representative Oil Red O and H&E liver staining. Scale bar=100 μm. (E) Body mass, (F) caloric consumption, (G) water intake, and (H) daily locomotor activity (n=4–8). Two-way ANOVA with Tukey’s post-hoc test for all. *p<0.05 vs. normal chow, #p<0.05 vs. high fat diet sham.