Figure 3. Effect of donor age and diamide on red blood cell ATP release in normoxia and hypoxia.
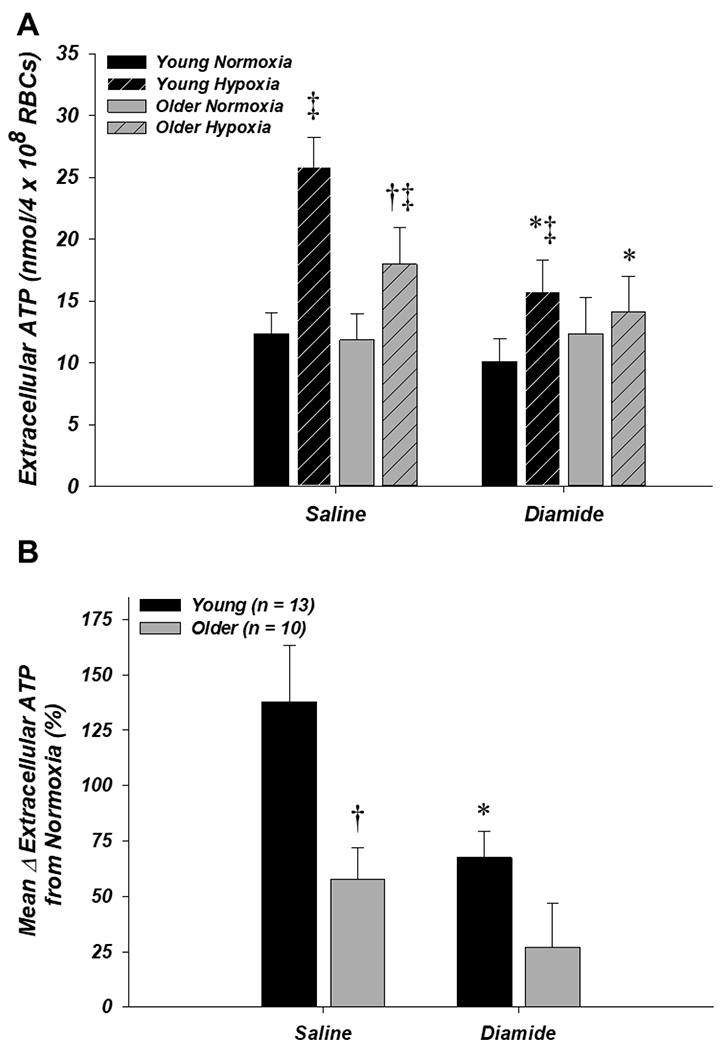
A: extracellular ATP (i.e., ATP release) from RBCs of older adults was significantly lower compared to young adults during hypoxia with saline (control) but not diamide, as diamide significantly decreased extracellular ATP during hypoxia from RBCs of both age groups. B: the mean percent increase in extracellular ATP from normoxia to hypoxia was impaired from RBCs of older adults in the saline condition. Incubation with diamide significantly decreased ATP release from RBCs of young adults such that it was no longer different from older adults. *P < 0.05 vs. saline (within age); †P < 0.05 vs. young (within condition); ‡P < 0.05 vs. normoxia (within condition)
