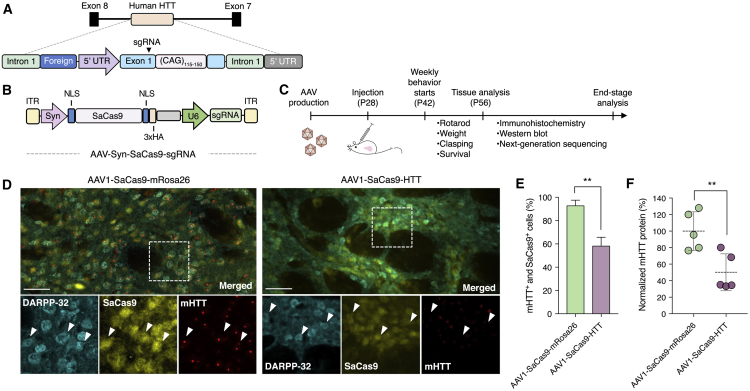
Figure 2.
In Vivo Disruption of the Mutant HTT Gene in R6/2 Mice
(A) Cartoon of the human HTT transgene located in Gm12695 (predicted gene 12695) on chromosome 4 in R6/2 mice. Arrowhead indicates approximate location of sgRNA binding site. (B) Schematic of the AAV vector. ITR, inverted terminal repeat; hSyn, human synapsin promoter; NLS, nuclear localization sequence; 3xHA, three tandem repeats of the human influenza hemagglutinin (HA) epitope tag. (C) Timeline for in vivo studies. (D) Immunofluorescent staining of striatal sections 4 weeks after R6/2 mice were injected with 6 × 1010 vector genomes of (left) AAV1-SaCas9-mRosa26 or (right) AAV1-SaCas9-HTT. Insets show high-magnification images. Arrowheads indicate representative DARPP-32+ and SaCas9+ cells with (left) high or (right) reduced mutant HTT (mHTT) protein. Images were captured using identical exposure conditions. Scale bars, 50 μm. (E) Quantitation of immunohistochemical results from R6/2 mice injected with AAV1-SaCas9-HTT (n = 3) or AAV1-SaCas9-mRosa26 (n = 3). (F) Normalized mutant HTT protein in striatal lysate 4 weeks after R6/2 mice were injected with 6 × 1010 vg of AAV1-SaCas9-mRosa26 or AAV1-SaCas9-HTT (n = 5). **p < 0.01, unpaired t test. Error bars indicate SD. All injections were performed on 28-day-old animals.