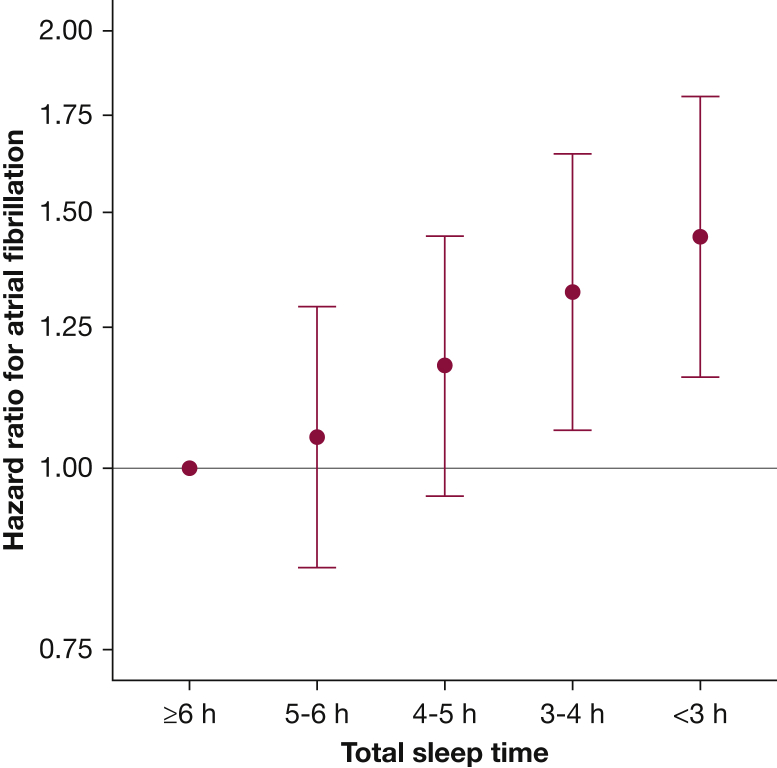
Figure 3.
Total sleep time as a predictor of incident atrial fibrillation. Hazard ratios for incident atrial fibrillation by total sleep time, with 95% CIs relative to patients sleeping ≥ 6 h. They were adjusted for age, age-squared, sex, center, BMI, congestive heart failure, hypertension, COPD, coronary artery disease, peripheral arterial disease, cerebrovascular disease, and apnea-hypopnea index. P < .001 for test of linear trend.