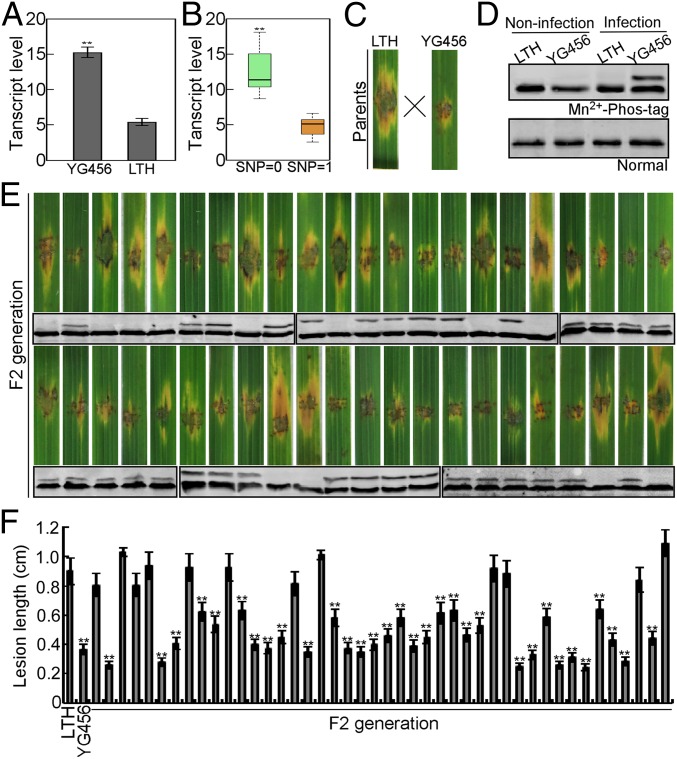
Fig. 2.
Genetic association between the SNP pattern and expression of LHCB5 and the inheritance of LHCB5 phosphorylation. (A) The transcript analysis of LHCB5 in YG456 and LTH. qRT-PCR on LHCB5 in YG456 in comparison with LTH. (B) The transcript analysis of LHCB5 in an F2 population derived from a cross between YG456 and LTH. The expression level of 44 progeny was analyzed by qRT-PCR. (C) Blast resistance of LTH and YG456 plants. The leaves of 4-wk-old plants were inoculated using method of punch. Photos were taken at 6 dpi. (D) Detection of LHCB5 phosphorylation in LTH and YG456. LTH and YG456 plants were inoculated with (infection) or without (noninfection) Guy11 after 48 hpi. The protein extracts were subjected to Phos-tag SDS/PAGE and normal SDS/PAGE followed by immunoblotting with the anti-LHCB5 polyclonal antibody. (E) Rice blast resistance is correlated with phosphorylation assess in the F2 generation of LTH and YG456. Blast resistance of 44 F2 generations using punch inoculation. Phosphorylation assay was performed as above. (F) Lesion length was measured 6 dpi. Values are the means of 3 replications, and error bars represent the SD (n = 3). The asterisks indicate a significant difference according to Student’s t test (P < 0.01).