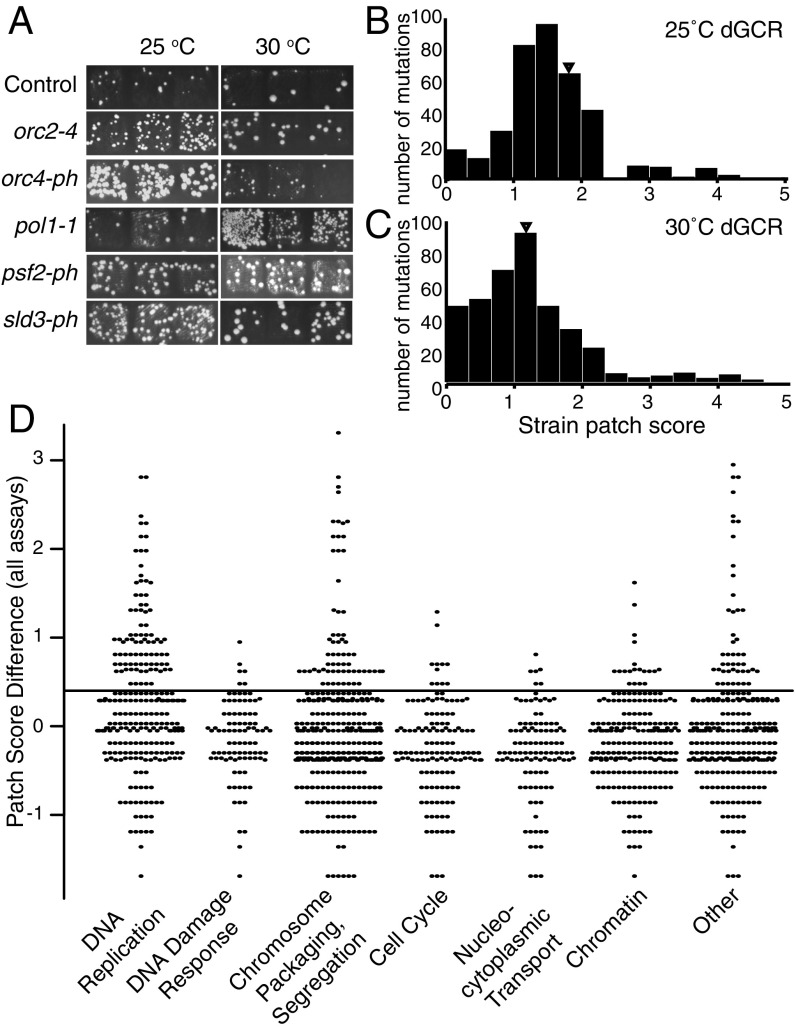
Fig. 1.
Identification of essential genome instability suppressing (eGIS) genes in S. cerevisiae. (A) Example patches of haploid strains containing the dGCR assay at permissive (25 °C) and semipermissive (30 °C) temperatures after replica plating onto GCR-selecting media. (B and C) Histograms of average strain patch scores for the dGCR assay at 25 °C (B) and 30 °C (C). The triangle indicates the position of the average patch score of the control (leu2Δ) strain. (D) Beehive plot of the difference in average patch score for each mutant strain relative to the control strain for the dGCR and sGCR assays measured at 25 °C and 30 °C (Dataset S1); an increase of 0.4 (horizontal line) was previously established as the cutoff for significance (11). Mutant strains were classified by the function of the affected gene.