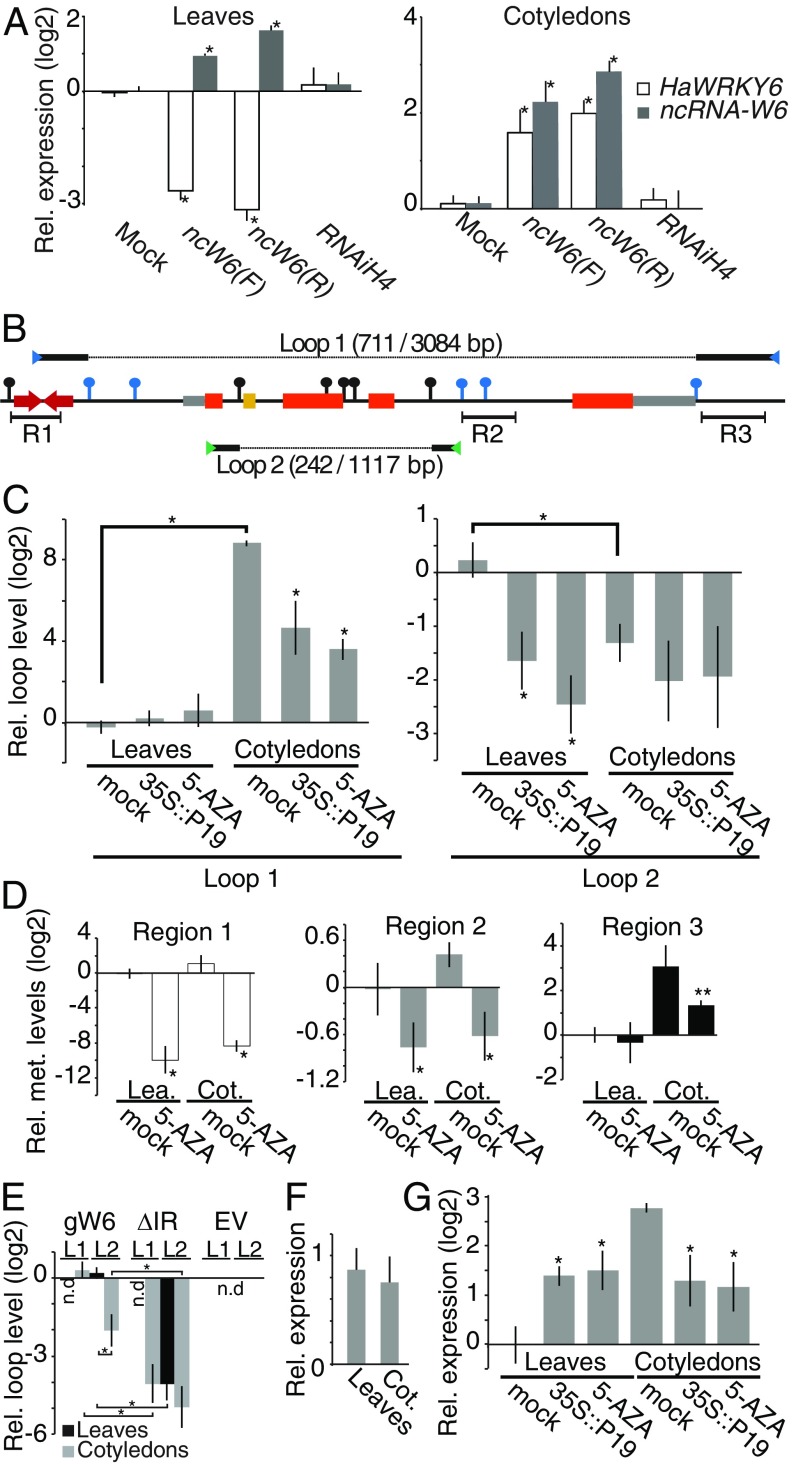
Fig. 3.
The ncW6 modulates chromatin topology through alternative loop formation at the HaWRKY6 locus. (A) HaWRKY6 and ncW6 transcript levels in transiently transformed sunflowers expressing the ncW6 cloned in each orientation. A nonrelated hairpin structure (RNAiH4) was used as a negative control. (B) Schematic of the HaWRKY6 genomic region. HindIII (black pins) and MspI (blue pins) restriction sites. R1–R3 note sRNA mapping regions. Blue and green arrowheads indicated primers used to detect L1 and L2, respectively. Solid lines on the top and bottom of the scheme show the obtained sequence after 3C ligation while the dashed line indicates the missing sequence. The obtained and undigested sequence length is given in brackets. (C) Quantification of loop formation by 3C-qPCR in leaves and Cots of mock controls and plants treated with 5-AZA or expressing P19. (D) Chop-qPCR of genomic DNA from mock or treated leaves and Cots to quantified DNA methylation in region 1 (white), regions 2 (gray), and region 3 (black). (E) Loop formation (L1 and L2) in leaves and Cots transformed with a full-length copy of the HaWRKY6 genomic locus (gW6), a version excluding the ncW6 (ΔIR) or an empty vector (EV). (F) HaWRKY6 promoter activity as measured by RT-qPCR quantification of transiently transformed sunflower expressing the reporter gene GUS under the HaWRKY6 promoter. (G) HaWRKY6 transcript levels as measured by RT-qPCR in samples extracted from 5-AZA-treated or transiently transformed sunflower tissues. In all panels, error bars represent 2 × SEM, P values of less than 0.05 (**) or 0,01 (*) in a 2-tailed unpaired t test were considered significant.