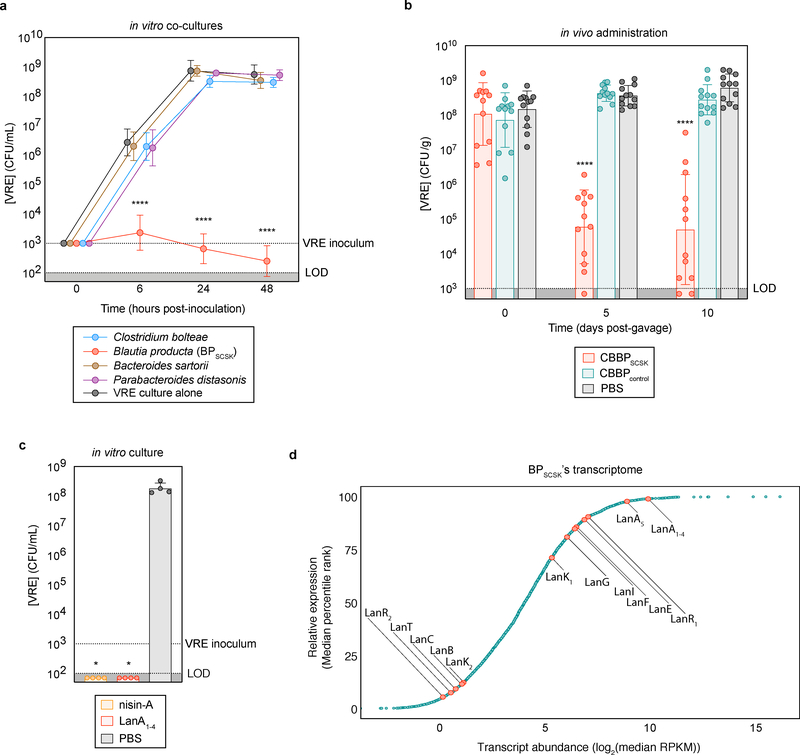
Figure 1 |. BPSCSK expresses a lantibiotic in vivo that inhibits VRE.
a, VRE was co-cultured in vitro with each CBBP isolate (n = 15 biologically independent samples/3 independent experiments) and monitored for growth. b, antibiotic-treated, VRE dominated mice (n = 12 mice/3 independent experiments) received treatment by oral gavage containing CBBP, CBBPcontrol, or PBS. VRE colonization was monitored by CFU quantification in fecal samples. c, VRE was inoculated in culture broth with commercial nisin-A (100 μM), purified BPSCSK’s LanA1–4 lantibiotic (100 μM), or PBS (n = 4 biologically independent samples/2 independent experiments). VRE CFUs were enumerated 8 hours post-inoculation. d, RNA-Seq analysis was performed on cecal content from mice treated with CBBP (n = 3 mice/1 independent experiment). VRE (ATCC 700221) was used in experiments shown in panels a-c. All statistical analyses were performed using the Mann-Whitney rank sum test (two-tailed) comparing experimental conditions to a negative control. **** p-value < 0.0001, * p-value < 0.05 (= 0.0286). Data points (geometric mean), error bars (geometric s.d.) (a); median, error bars (range) (b); center value (geometric mean), error bars (geometric s.d.) (c), data points (median) (d).