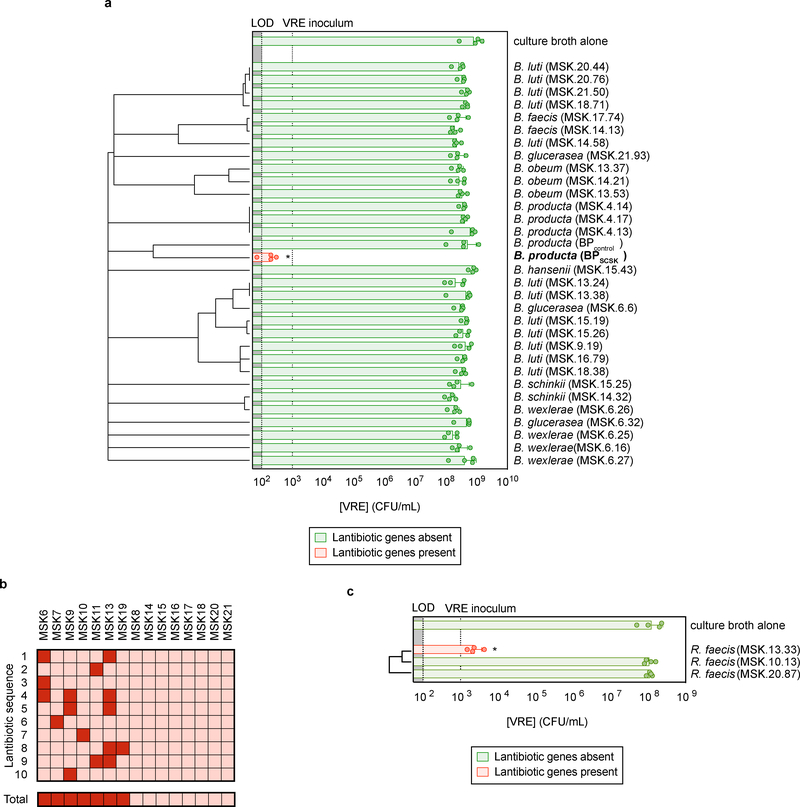
Figure 3 |. Lantibiotic genes are present in human microbiomes of healthy individuals and gut resident, lantibiotic-producing species inhibit VRE.
a, Microbiota-derived Blautia species were whole genome sequenced, assembled, annotated, and mined for lantibiotic precursor sequences. VRE was inoculated in conditioned-media from 39 strains (n = 4 biologically independent samples/4 independent experiments) and monitored for growth. b, Lantibiotic detection from shotgun sequencing of human fecal samples (n = 15 fecal samples). c, 421 commensal biobank isolates were whole genome sequenced, assembled, annotated, and mined for lantibiotic precursor sequences to identify a strain of Ruminococcus faecis encoding a homologous lantibiotic. VRE was inoculated in conditioned-media from 3 strains of R. faecis cultures (n = 4 biologically independent samples/4 independent experiments) with or without detected lantibiotic genes and VRE growth was monitored 8 hours post-inoculation. VRE (ATCC 700221) was used in experiments shown in panels a, c. All statistical analyses were performed using the Mann-Whitney rank sum test (two-tailed) comparing experimental conditions to a negative control. * p-value < 0.05 (= 0.0286). Center values (geometric mean), error bars (geometric s.d.) (a, c).