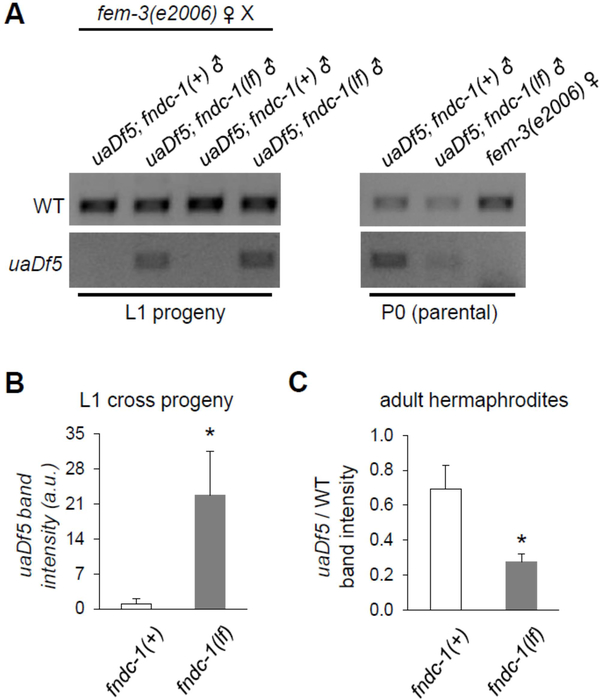
Figure 2 -. The paternal mitochondrial genome is detectable in cross progeny of fndc-1(lf) males.
uaDf5 is a mitochondrial haplotype with a large deletion in the mitochondrial genome that can be detected by PCR.
A The first four lanes contain ethidium bromide stained gel-separated PCR products from ~100 L1 cross-progeny of fem-3(e2006) females that had been mated to either fndc-1(+) or fndc-1(lf) males containing uaDf5 mtDNA. These data are two replicates of six indepenent experiments that were performed. The second set of three lanes are similar PCR reactions from the paternal and maternal worms that were used to create the cross-progeny. Note that amplification cycles (generally 25–35) have been optimized for each of the primer combinations, whether used as pairs or in triplicate, for L1 versus P0 generations, and for multiple versus single worms (see Methods). As such, band intensities are only directly comparable within the boundaries of each image.
B uaDf5 in L1 cross-progeny from fndc-1(+) or fndc-1(lf) males and fem-3(e2006) hermaphrodites. The band intensity for the uaDf5 PCR product was determined and normalized to the wildtype PCR product to control for total mtDNA content. The data represents the average values from six independent experiments (mean ± SEM; *p < 0.05; t-test).
C Relative uaDf5 abundance in fndc-1(+) and fndc-1(lf) adult hermaphrodites. The data (for which the PCR reactions are not shown) represents the average values from three independent experiments (mean ± SEM; *p < 0.05; t-test).