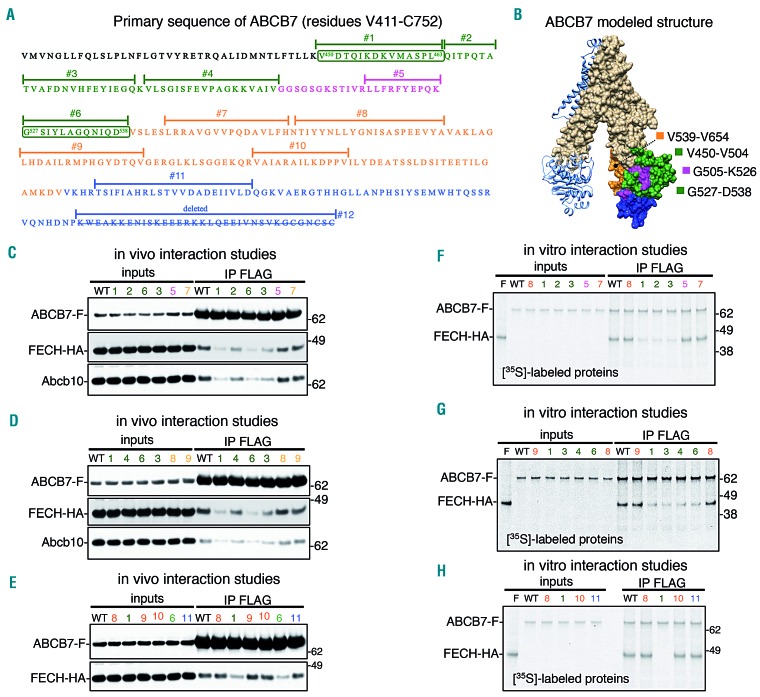
Figure 6.
Mutational analysis of the C-terminal domain of ABCB7 identified the region V450-D538 as being involved in binding ferrochelatase. (A) Primary sequence of the C-terminal domain of ABCB7. (B) Modeled crystal structure of ABCB7. The numbered peptide sequences in (A) and the corresponding colored regions in (B) refer to the amino acid residues that were subjected to alanine scanning mutagenesis to assess their involvement in interacting with FECH. (C-E) Immunoprecipitation (IP) of FLAG-tagged ABCB7 wildtype (B7) or the mutants, as indicated, expressed in G1E-ER4 cells that had been silenced for 3 days to knockdown the expression of endogenous Abcb7 and that co-expressed HA-tagged FECH. Mutants 1, 2, 3, 4 and 6 of ABCB7 [green peptides and domains in (A) and (B), respectively] showed significantly decreased binding to FECH and to Abcb10. (F-H) In vitro pull-down assays of 35S-labeled FLAG-tagged ABCB7 wildtype (B7) or mutants, as indicated, in the presence of 35S–FECH (F) confirmed the results obtained in vivo (C-E) and demonstrated that binding of FECH to ABCB7 was through direct physical interaction. (C-E, n=6. F-H, n=4). See also Online Supplementary Figure S17 for densitometries of immunoblots and statistical analyses.