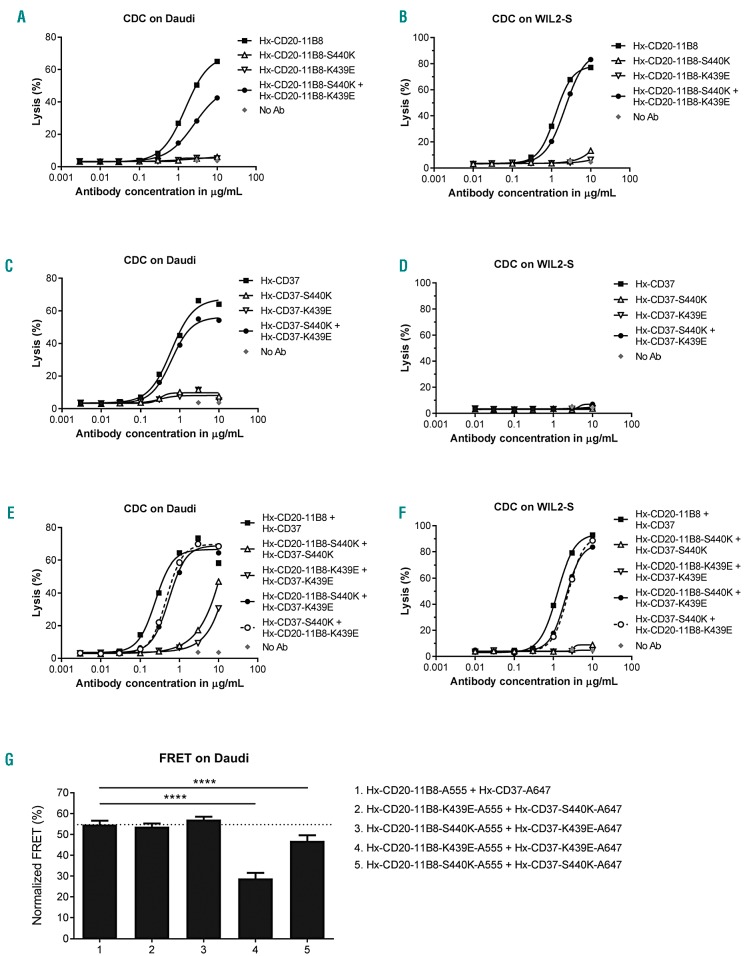
Figure 5.
Hexamerization-enhanced CD20 and CD37 mAb cooperate in complement-dependent cytotoxicity (CDC) through Fc-mediated clustering in hetero-hexamers. The effect of introducing Fc-Fc inhibiting mutations S440K and K439E on the CDC induction of hexamerization-enhanced type II CD20 mAb 11B8-derived Hx-CD20-11B8 on Daudi cells (A) and WIL2-S cells (B), hexamerization-enhanced CD37 mAb 37.3-derived Hx-CD37 on Daudi (C) and WIL2-S cells (D) and the mAb combinations thereof on Daudi (E) and WIL2-S cells (F). Cells were opsonized with concentration series of Hx-CD20-11B8 and Hx-CD37 variants in the presence of 20% NHS. CDC induction is expressed as the percentage lysis determined by the fraction of propidium iodide (PI)-positive cells. Representative examples of two (WIL-2S) and three replicates (Daudi) are shown. (G) The effect of introducing Fc-Fc inhibiting mutations S440K and K439E on the molecular proximity of Hx-CD20-11B8 and Hx-CD37 variants on the cell membrane of Daudi cells. Daudi cells were incubated with 10 μg/mL A555-conjugated Hx-CD20-11B8 variants and 10 μg/mL A647-conjugated Hx-CD37 variants for 15 minutes at 37°C. FRET was calculated from the mean fluorescence intensity values as determined by flow cytometry. Data shown are mean and Standard Deviation of six replicates collected from three independent experiments. ****P<0.0001.