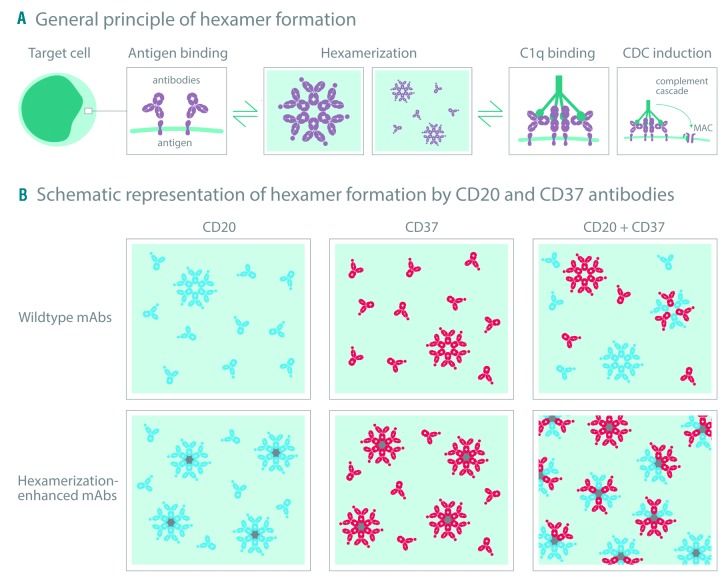
Figure 7.
Model for Fc-mediated clustering of CD20 and CD37 monoclonal antibodies (MAbs) in hetero-hexamers upon binding to the cell surface. (A) mAbs naturally cluster into hexameric complexes upon antibody binding to a cognate antigen on a target cell, thereby providing a docking site for C1q binding and complement-dependent cytotoxicity (CDC) induction. (B) Upon binding of mAbs targeting two different coexpressed antigens on the plasma membrane that (are able to) colocalize, hetero-hexameric antibody complexes are formed consisting of both mAbs, providing a docking site for C1q binding and CDC induction. Introducing hexamerization-enhancing mutations can increase Fc-mediated clustering of mAbs, both into homo-and hetero-hexameric antibody complexes on the cell surface, thereby increasing the number of C1q docking sites and further potentiating CDC.