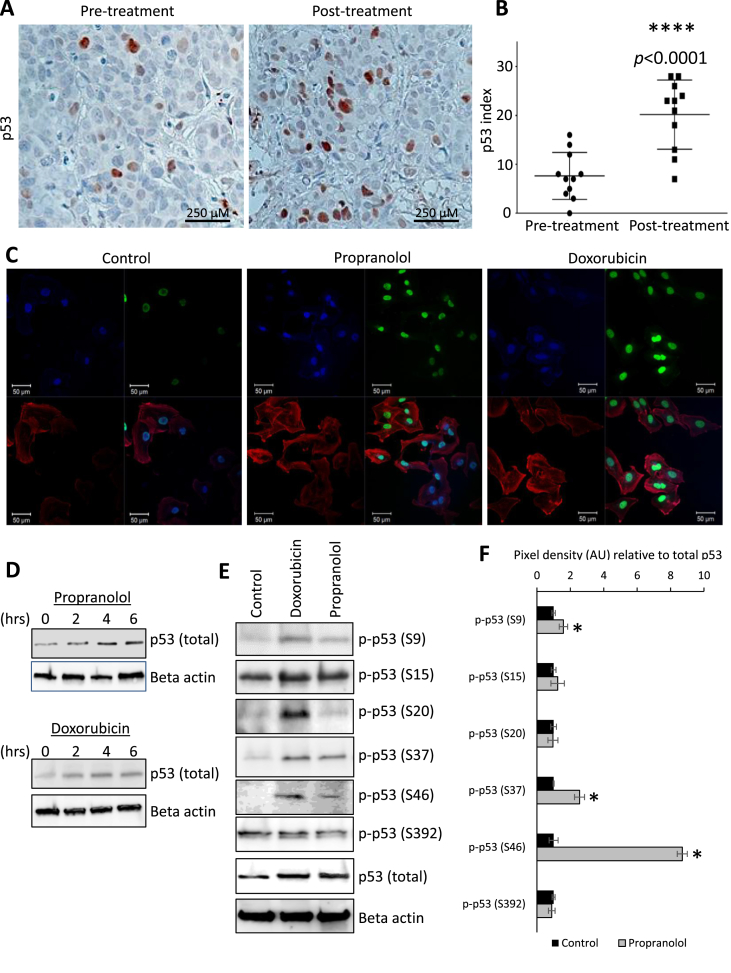
Fig. 3.
Propranolol modulates p53 steady state protein levels and post-translational modifications. (A & B) IHC and graphical representation for p53 protein performed on tissues from the diagnostic biopsy (pre-treatment) and surgical resection (post-treatment). Brown staining indicates p53 antigenicity. Ten random vision fields were counted per condition. (C) Immunofluorescent staining for p53 (green), Hoechst 33342 nuclear counterstain (blue), and rhodamine-conjugated phalloidin as an actin counterstain (red) in MDA-MB-231 cells treated with vehicle control or 40 μM propranolol. Three μM doxorubicin was added as a positive experimental control. (D) Immunoblotting for p53 protein levels in MDA-MB-231 cells treated with 40 μM propranolol over a 6 h time course. Three μM doxorubicin was added as a positive experimental control. (E & F) Immunoblotting of p53 phosphorylation events in MDA-MB-231 cells treated with vehicle control or 40 μM propranolol for 6 h. Three μM doxorubicin was added as a positive experimental control. For quantification, phospho-p53 was normalized relative levels of both total p53 and actin. AU indicates arbitrary units.