Figure 3.
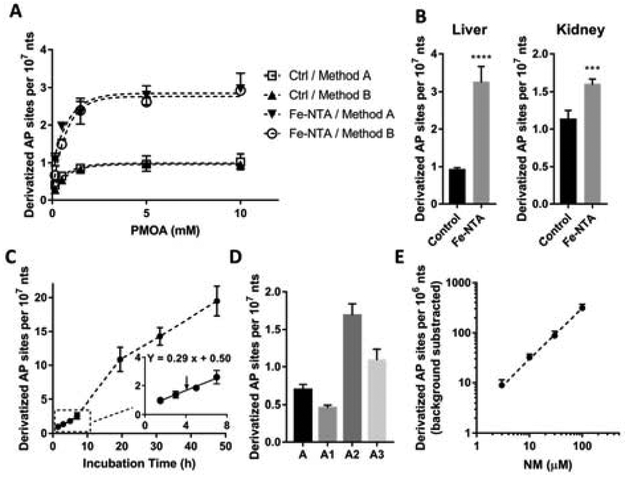
(A) Derivatization of AP sites in rat liver nuclei. Rats were sacrificed 6 h after intraperitoneal injection with Fe-NTA (15 mg Fe/kg) and vehicle (Ctrl group). AP sites were derivatized by the nuclear lysate-derivatization method (method A) or nucleic acid-derivatization method (method B). Each value represents the mean ± SD, n = 3. (B) AP site level in rat livers and kidneys after administration of Fe-NTA (grey bar) or vehicle (black bar). n = 4. Two-tailed t test p < 0.0001 (****), p < 0.001 (***). (C) Spontaneous depurination rate measured in untreated rat liver nuclei lysate (n=3). (D) AP site level in DNA isolated/derivatized by different methods. A. After nuclear isolation, conduct proteolysis for 1.5 h and then AP site derivatization for 1.5 h. A1: After nuclear isolation, conduct AP site derivatization and proteolysis together for 1.5 h. A2: Treat nuclei with RNases for 1.5 h, proteinase K for 2 h, and precipitate excess proteins. Precipitate DNA with salt/isopropanol and immediately derivatize the isolated DNA. A3: Unlike method A2, DNA pellet was precipitated under −20 °C overnight before derivatization. n = 4. (E) Isolated rat liver DNA was incubated with NM at 37 °C for 1 h, followed by neutral hydrolysis for 5 h (pH 7.4). n = 3. The background level of AP sites by neutral hydrolysis (6.5 ± 1.5/107 nts) was subtracted.
